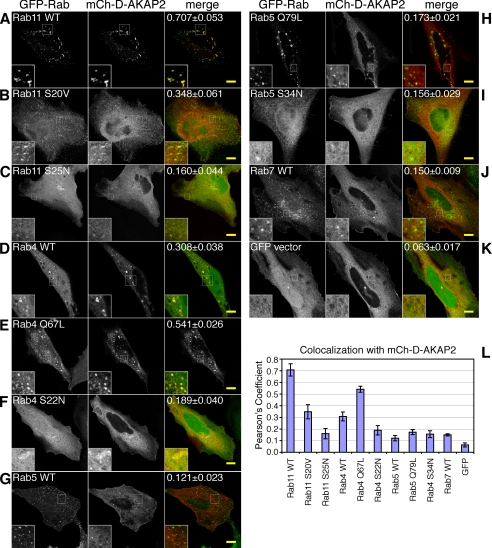
FIGURE 2.
D-AKAP2 is recruited to endosomes by Rab4 and Rab11. HeLa cells were transfected with mCherry-D-AKAP2 together with GFP-tagged Rab proteins or their GDP- or GTP-locked mutant forms: Rab11 WT (A), GTP-locked Rab11 S20V (B), GDP-locked Rab11 S25N (C), Rab4 WT (D), GTP-locked Rab4 Q67L (E), GDP-locked Rab4 S22N (F), Rab5 WT (G), GTP-locked Rab5 Q79L (H), GDP-locked Rab5 S34N (I), Rab7 WT (J), and GFP vector (K). D-AKAP2 on endosomes colocalized extensively with Rab11 (A) and Rab4 (D), the two Rab proteins most involved in regulating the endocytic recycling compartment, but not with Rab5 (G) or Rab7 (J). Co-expression with either Rab4 or Rab11 caused increased localization of D-AKAP2 on endosomes; this was particularly true for Rab11 WT, which tended to accumulate with D-AKAP2 on enlarged endosomes (A). Scale bars, 10 μm. Quantification of endosomal colocalization was determined as described under “Experimental Procedures” as the Pearson's coefficient for the top 5% of pixels within the cell. The value given in the merge panel represents the average ± S.E. for 6–8 confocal images and is depicted in the graph (L).