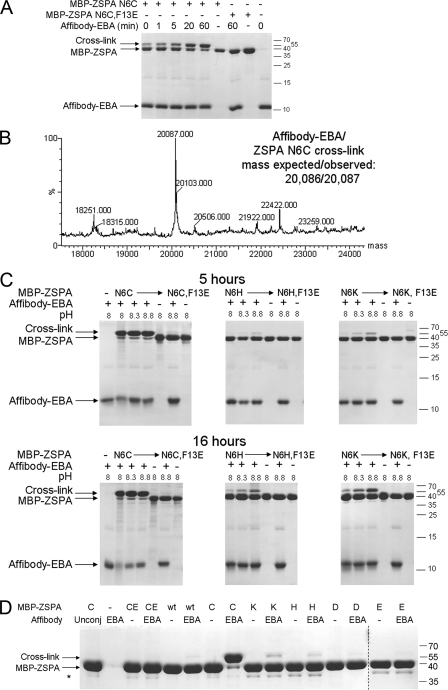
FIGURE 2.
Electrophilic affibody covalent bond formation. A, speed of covalent bond formation to N6C. We incubated affibody-EBA with MBP-ZSPA N6C for the indicated times at 37 °C at pH 8.0 and analyzed cross-linking by SDS-PAGE. A point mutant of MBP-ZSPA that disrupted the initial non-covalent interaction (N6C F13E) was a negative control. Bands corresponding to affibody-EBA, MBP-ZSPA, and cross-links are indicated. B, mass spectrometry to verify cross-link between affibody-EBA and ZSPA N6C. C, pH-dependence of reactivity. We incubated affibody-EBA with MBP-ZSPA N6C, N6H, or N6K for 5 h (top row) or 16 h (bottom row) at pH 8.0, 8.3, or 8.8 and determined cross-linking by SDS-PAGE. Negative controls are shown without affibody-EBA, without any MBP-ZSPA, or with non-interacting F13E variants. D, reactivity of all potential nucleophilic side chains with affibody-EBA. MBP-ZSPA wild-type (wt) or with various mutations at position Asn-6 was incubated with or without affibody-EBA at pH 8.3 for 4 h at 37 °C and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining. Lane 1 is a control where affibody D36C is unmodified with EBA (Unconj). CE is the N6C F13E non-interacting negative control. An asterisk relates to small amounts of a proteolytic fragment from cleavage of the linker between MBP and ZSPA. The dotted line indicates samples run on a different gel at the same time.