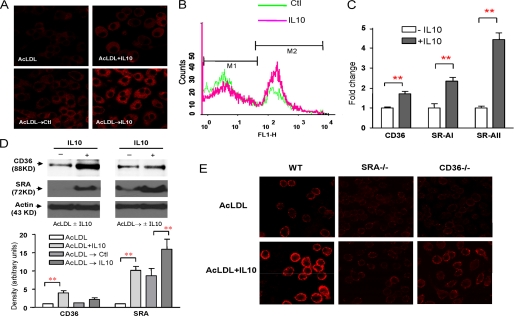
FIGURE 1.
IL10 increases Dil-AcLDL uptake through up-regulation of expression of scavenger receptors. A, resting macrophages (top) and lipid-laden macrophages (bottom) were treated either with AcLDL, with AcLDL plus IL10, with medium alone (control), or with IL10 for 24 h followed by an assay to determine the Dil-AcLDL uptake. Dil-AC-LDL uptake was determined by confocal microscopy. B, histograms of Dil-Ac-LDL uptake between control (green line) and IL10 (red line) were overlaid. The lipid-laden Raw cells were treated with either medium alone (control) or IL10 for 24 h, followed by flow cytometry analysis. C, transcripts for scavenger receptors (CD36, SR-AI, and SR-AII) were detected by real-time PCR in lipid-laden macrophages treated with medium (blank column) or with IL10 (gray column) for 24 h. The results are representative of at least three independent experiments, and values are expressed as the -fold change in abundance ± S.E. D, IL10 up-regulates CD36 and SR-A protein expression. Resting Raw cells or lipid-laden Raw cells were treated as indicated for 24 h. Expression of CD36 and SR-A protein was examined by immunoblot analysis using rabbit anti-CD36 antibody and rat anti-mouse CD204 antibody. Representative results from three experiments are shown (top). The densities of bands corresponding to CD36 and SR-A were quantitated using an image densitometer. The data shown are band densities in arbitrary optical density units from three repeated experiments (bottom). E, IL10 enhances the Dil-AcLDL uptake through scavenger receptors. Bone marrow-derived macrophages from either SR-A- or CD36-knock-out mice or C57BL/6 mice (control) were treated with either AcLDL or AcLDL plus IL10 for 24 h. Dil-AC-LDL uptake was determined by confocal microscopy. WT, wild type.