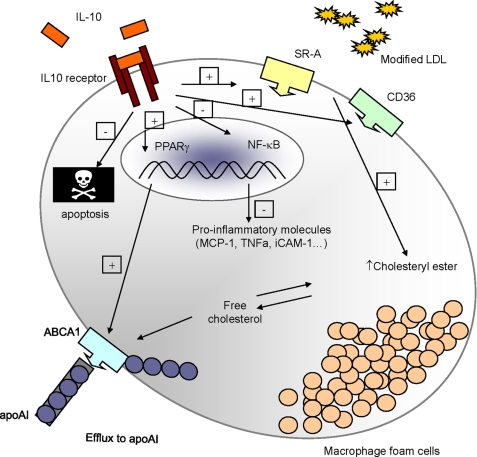
FIGURE 7.
Schematic overview of the protective role of IL10 during atherosclerosis involving regulation of lipid metabolism in macrophages. Upon binding to its receptor, IL10 up-regulates scavenger receptors, such as SR-A (SR-AI and SR-AII) and CD36, which account for a dramatic increase in modified LDL uptake by macrophages, promoting cholesteryl ester accumulation and foam cell formation. Moreover, IL10 promotes ABCA1-mediated free cholesterol efflux to apoAI in a PPARγ-dependent manner. Despite its effect on promoting foam cell formation, IL10 markedly represses the expression of proinflammatory molecules, such as TNFα, MCP-1, and ICAM-1, presumably through an inhibition of NF-κB activity, as documented before (45), and diminishes apoptosis in the lipid-laden foam cells.