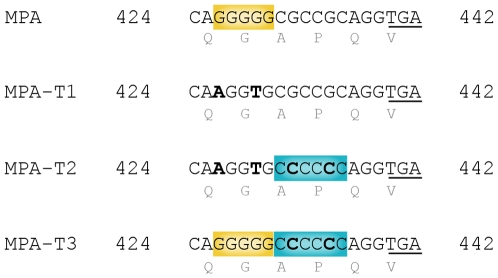
Figure 1. Site directed mutagenesis on the mucA gene.
A fragment of the P. aeruginosa mucA gene where the site directed mutagenesis was performed is shown. Base changes (bold face) were designed in order to maintain the amino acidic sequence unaltered (shown below), and codons were chosen that are commonly used by P. aeruginosa. The premature stop codon generated by a hypothetical −1 bp deletion between positions 426 and 436 of mucA is underlined. Wild type mucA allele from MPA strain with G5SSR426 is highlighted in yellow. The mucAT1 allele from strain MPA-T1 was generated by replacing G-to-A at 426 and G-to-T at 429, thus eliminating G5SSR426. The mucAT2 allele from strain MPA-T2 was generated by replacing G-to-A at 426 and G-to-T at 429 (eliminating G5SSR426), and G-to-C at 432 and 435 to generate C6SSR431 (highlighted in blue). The mucAT3 allele from strain MPA-T3 was generated by replacing G-to-C at 432 and 435 to generate C6SSR431 (highlighted in blue), and maintaining G5SSR426 (highlighted in yellow) unaltered.