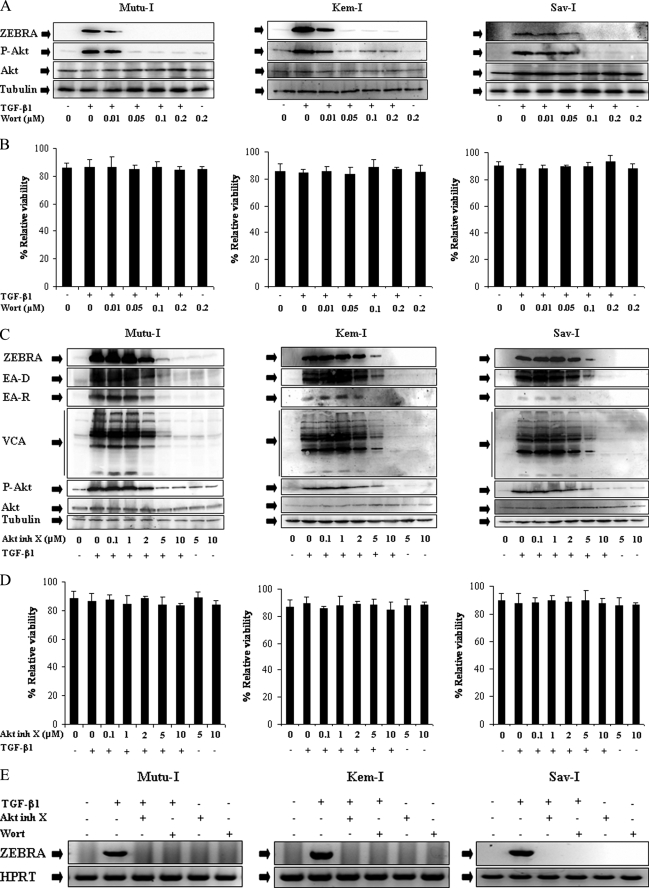
FIGURE 1.
Inhibitors of PI3-K/Akt signaling pathway abolished TGF-β1-induced ZEBRA expression. A and C, Mutu-I, Kem-I, and Sav-I cells were treated with increasing concentration of wortmannin (Wort) (0.01, 0.05, 0.1, or 0.2 μm) (A) or Akt inhibitor X (Akt inh X) (0.1, 1, 2, 5, or 10 μm) (C) for 1 h, prior to incubation with TGF-β1 (2 ng/ml). Seventeen hours later, the cells were harvested and lysed. Equal amounts of protein were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies to ZEBRA, phospho-Akt, Akt, and tubulin. B and D, viability assay was performed with the LIVE/DEAD reduced biohazard viability/cytotoxicity kit (Molecular Probes, Invitrogen). The ability of this kit to detect cell death was controlled using a treatment with 0.4 mm of MnCl2 (not shown). E, RT-PCR assay of ZEBRA was performed. 3 μg of total RNA from Mutu-I, Kem-I, and Sav-I cells pretreated, respectively, with 0.05, 0.05, and 0.1 μm of wortmannin or 10 μm of Akt inhibitor X for 1 h and then stimulated with TGF-β1 (2 ng/ml) for 17 h were reverse transcribed. cDNA coding for ZEBRA was then analyzed by PCR; cDNA of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT) was used as an internal control.