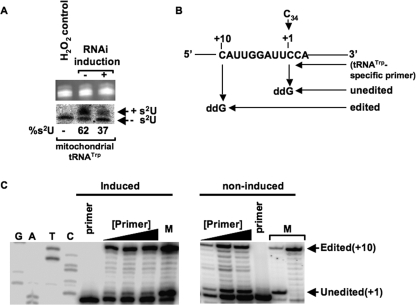
FIGURE 6.
Knockdown of Nfs increases editing of mitochondrial tRNATrp. A, mitochondrial RNA isolated from 2 × 109 cells from noninduced and RNAi-induced cells was separated electrophoretically on an APM gel. The tRNA portion of the ethidium bromide-stained APM gel (top) was used as a loading control. Northern blot analysis probing for tRNATrp is shown at bottom. Bands corresponding to thiolated tRNA and nonthiolated tRNAs are indicated. H2O2 is used as a control to show complete oxidation of thiolation, eliminating the mobility shift. Percent thiolation of the tRNA is shown below the panel and calculated as described previously. B, schematic of the poisoned primer extension assay to measure editing levels. C, poisoned primer extension analysis followed by PAGE. Left panel shows a nonspecific sequencing ladder for orientation and the primer extension using mitochondrial RNA from Nfs knockdown cells. Right panel shows control reactions with mitochondrial RNA from noninduced RNAi cells. Bands representing stops from the edited and unedited are shown to the right. M denotes a marker lane where the primer band, unedited band, and edited band are shown, and in this lane the products were generated by performing poisoned primer extension on tRNATrp in vitro transcripts containing either a C34 (unedited) or a U34 (edited). These control reactions using transcripts were carried out simultaneously but in a separate primer extension reaction. Primer corresponds to lanes where primer alone was loaded. Black triangles denote increasing concentrations of primer used in the assay to ensure linearity during quantitation.