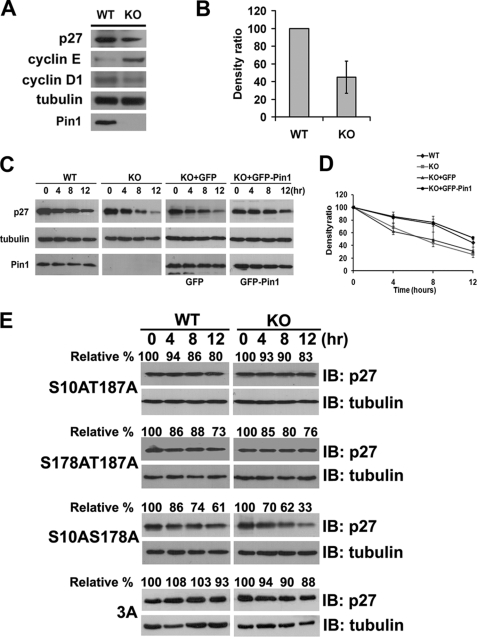
FIGURE 4.
Pin1 regulates p27Kip1 stability. A, immunoblotting analysis of the endogenous p27Kip1, cyclin E, and cyclin D1 levels in Pin1-WT and -KO MEFs. B, quantification of endogenous p27Kip1 levels shown in A, normalized to tubulin levels. C, protein stability assay of endogenous p27Kip1 in both Pin1-WT and -KO MEFs. Cells were starved for 36 h before their arrest at G0 phase. The cells were then treated with cycloheximide, harvested at 4-h intervals (left panel), and analyzed by immunoblotting. To confirm the function of Pin1 in regulating p27Kip1 stability, GFP-Pin1 and GFP vectors were re-introduced into Pin1-KO MEF cells, respectively, followed by a protein stability assay. D, densitometric analysis of the degradation assays from C, normalized to tubulin levels. E, protein stability assay of exogenous FLAG-p27Kip1 or its mutants in either Pin1-WT or -KO MEFs. Cells were treated with cycloheximide after 24 h of transfection and then harvested at 4-h intervals, followed by immunoblotting (IB) analyses. Tubulin was used as a loading control. KO, knock-out.