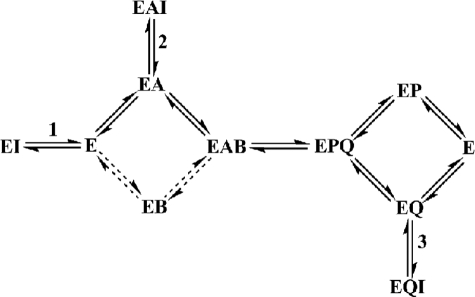
SCHEME 1.
Kinetic mechanism of GSNOR and the types of complexes formed by dodecanoic acid and the new GSNOR inhibitors in the kinetic pathway of GSNOR. GSNOR has a preferred pathway (shown by the heavy lines) through GSNOR·NADH complex (EA) in its random mechanism during the reduction of an aldehyde. The aldehyde (B), although it can bind to the free form of GSNOR (E), binds preferentially to the GSNOR·NADH complex to form the competent ternary complex (EAB). The ternary complex undergoes catalysis to form the products, NAD+ (Q) and alcohol (P). During the release of the products, either of the products can leave the enzyme. An inhibitor binding the GSNO binding site can bind to the free GSNOR (step 1), GSNOR·NADH (step 2), or GSNOR·NAD+ (step 3) binary complexes to form EI, EAI, and EQI complexes, respectively.