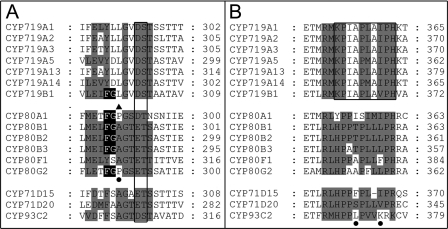
FIGURE 7.
Substrate recognition site comparison. A, in the SRS4 substrate recognition site comparison, the highly conserved cytochrome P450 motif (D/E)T is boxed. The black background in SRS4 is the FG motif shared by the tetrahydrobenzylisoquinoline binding cytochromes P450. The filled triangle indicates the amino acid residue in SRS4 that distinguishes the CYP80 hydroxylases from the phenol-coupling enzymes. The filled circle indicates the position of the available mutation experiments: CYP80G2 P290A/P290G. The gray shading emphasizes the conservation of amino acids of CYP719s compared with CYP80Bs and other non-alkaloid transforming cytochromes P450 (CYP71s and CYP93). B, in the SRS5 substrate recognition site comparison, the KPIAPXXXPH motif thus far unique to the CYP719 family is boxed. The filled circles indicate the position of the available mutation experiments: CYP71D20 S368V; CYP71D15 F363I; CYP93C2 K375T. The gray shading in SRS5 emphasizes the differences in amino acids of CYP719s compared with CYP80Bs and other non-alkaloid transforming cytochromes P450 (CYP71s and CYP93). Accession numbers are provided in the legend to Fig. 6.