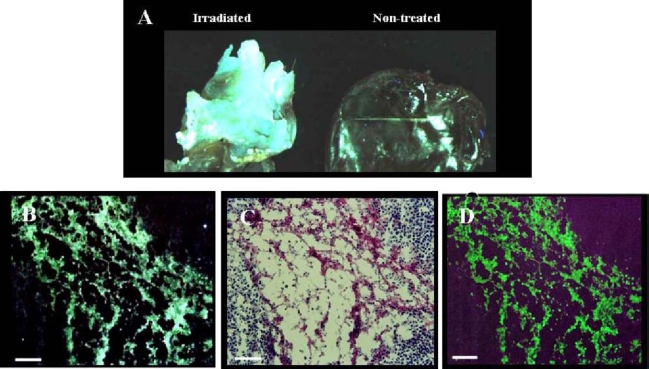
Fig. 9.
Uptake of NST-732 in vivo into B16 melanoma cells undergoing cell death. Lymphoma (LY-S) tumors were established in DBA mice. Mice were then treated by irradiation as described in the text. NST-732 was administered intravenously 72 h after the last dose of irradiation. Two hours later, mice were sacrificed, and tumors were subjected to whole-tumor and microscopic analysis. A. Ex-vivo imaging of the lymphoma control (non-radiated) tumor as compared to irradiated tumor, showing dramatic increase of NST-732 uptake upon irradiation. B. Fluorescent microscopy of an intense area of cell-death within the irradiated tumor, showing that the signal originated from intracellular accumulation of NST-732 in multiple individual cells undergoing cell death. C. H/E ex-vivo staining of a consecutive slide, showing that the uptake of NST-732 is in high correlation with area of cell death. D. TUNEL ex-vivo staining of a consecutive slide, showing co-localization of the cell-death TUNEL staining with NST-732 uptake, Scale bars: (A) 1 cm=300 µm; (B,C,D) 1 cm=100 µm