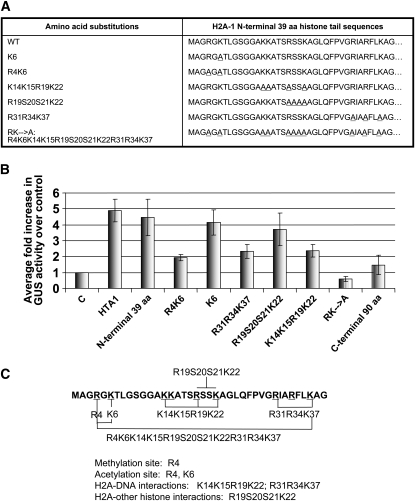
Figure 4.
The N-Terminal 39 Amino Acids of Histone H2A-1 Are Sufficient to Increase gusA Transgene Expression in Tobacco BY-2 Protoplasts.
(A) Amino acid sequence substitutions in the N-terminal H2A-1 region. Underlined amino acids in the right panel were substituted by Ala.
(B) Relative GUS activity in protoplasts cotransfected with a gusA expression cassette and various H2A-1 wild-type and mutant peptides. Numbers represent GUS activity relative to the empty vector control. Transfected cells were stained histochemically with X-gluc and examined microscopically 24 h later. More than 1000 cells were examined for each treatment. Error bars indicate se of at least three biological replicates.
(C) The first 39 amino acids of the histone H2A-1 protein. Specific amino acid mutations within this region are marked. Amino acids involved in acetylation, histone–DNA interactions, and histone–histone interactions are indicated.