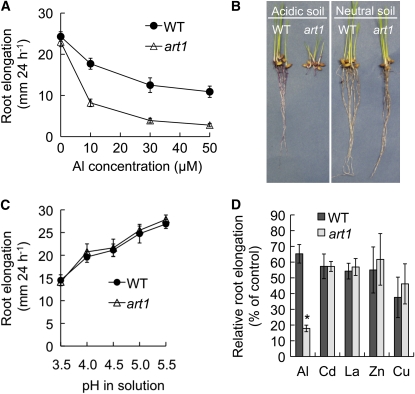
Figure 1.
Phenotype of the art1 Mutant.
(A) Response to Al. Five-day-old seedlings of both the wild-type rice and art1 were exposed to a 0.5 mM CaCl2 solution containing 0, 10, 30, or 50 μM AlCl3, pH 4.5, for 24 h. Data are means ± sd (n = 10).
(B) Growth on acid soil. Germinated seeds were sowed on acidic soil, pH 4.5, or neutral soil, pH 6.5, and grown for 6 d.
(C) Response to different pHs. Seedlings were exposed to a buffered solution at different pHs for 24 h. Data are means ± sd (n = 10).
(D) Effect of toxic metals on root elongation. Five-day-old seedlings were exposed to a 0.5 mM CaCl2 solution, pH 4.5, containing 0, 30 μM Al, 20 μM Cd, 5 μM La, 100 μM Zn, or 0.5 μM Cu in their chloride form for 24 h. Root elongation was measured before and after the treatment and relative root elongation, (root elongation with metals)/(root elongation without metals) × 100. Data are means ± sd (n = 8 to 10). The asterisk shows a significant difference between the wild type and art1 (P < 0.05 by Student's t test).