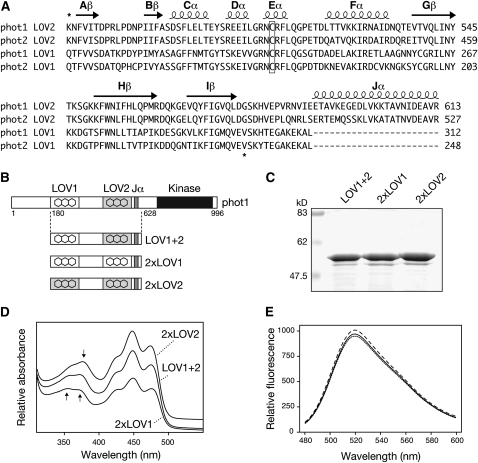
Figure 1.
Domain Swapping of Arabidopsis phot1 LOV Domains.
(A) Sequence alignment of LOV1 and LOV2 domains of Arabidopsis phot1 and phot2. Predicted secondary structure is indicated on top of the sequences. Regions used for domain swapping of phot1 LOV domains are indicated by asterisks. The conserved Cys required for photochemical reactivity is boxed.
(B) Schematic illustration showing regions of wild-type phot1 (LOV1+2) and 2xLOV1 and 2xLOV2 proteins generated. Relative positions of phot1 domain structures are indicated.
(C) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel showing purified preparations of wild-type phot1 (LOV1+2), 2xLOV1, and 2xLOV2. Sizes of molecular weight marker proteins are indicated on the left in kilodaltons.
(D) Absorption spectra of wild-type (LOV1+2), 2xLOV1, and 2xLOV2 proteins. Spectra are offset for clarity. Arrows indicate absorbance differences between 2xLOV1 and 2xLOV2 in the UV-A region of the spectrum.
(E) Fluorescence emission spectra of flavin fluorescence released upon denaturation of equal concentrations (0.4 mg mL−1) of wild-type LOV1+2 (solid line), 2xLOV1 (dotted line), and 2xLOV2 (dashed line).