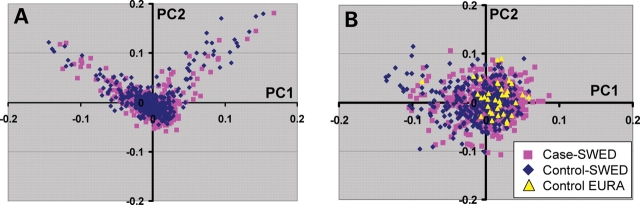
Figure 4.
Illustration of the use of PCA to select homogeneous sample sets. In this example, cases derived from a Swedish population and the controls were from both Sweden and European Americans. (A) The first and second principal component (PC1 and PC2) for the Swedish cases and control subjects. (B) Homogeneous subject set selected from Swedish cases and controls and 3447 European American subjects (same set as shown in Fig. 1). Color code indicates the origin of the subjects. The basic procedure was to remove Multivariate outliers based on Mahalanobis distance. The minimum covariance determinant (MCD) estimators of location and scatter of PCA scores of the entire dataset were calculated using R. The Mahalanobis distances were then calculated using the robust estimators, leading to robust distance (RD). For multivariate normally distributed data the RD values are approximately χ2 distributed with p degree-of-freedom (p is the number of dimensions). The procedure was applied in two steps. For the first phase of selection we removed case outliers using robust distance measurements. The significance level was set at α = 0.001 to remove the case outliers. A second phase repeating the same process was applied to the case–control dataset. This was based on the case-only robust estimators of location and scatter in order to define a more homogeneous case–control sample set. The significance level was set at α = 0.05 for this phase of the procedure.