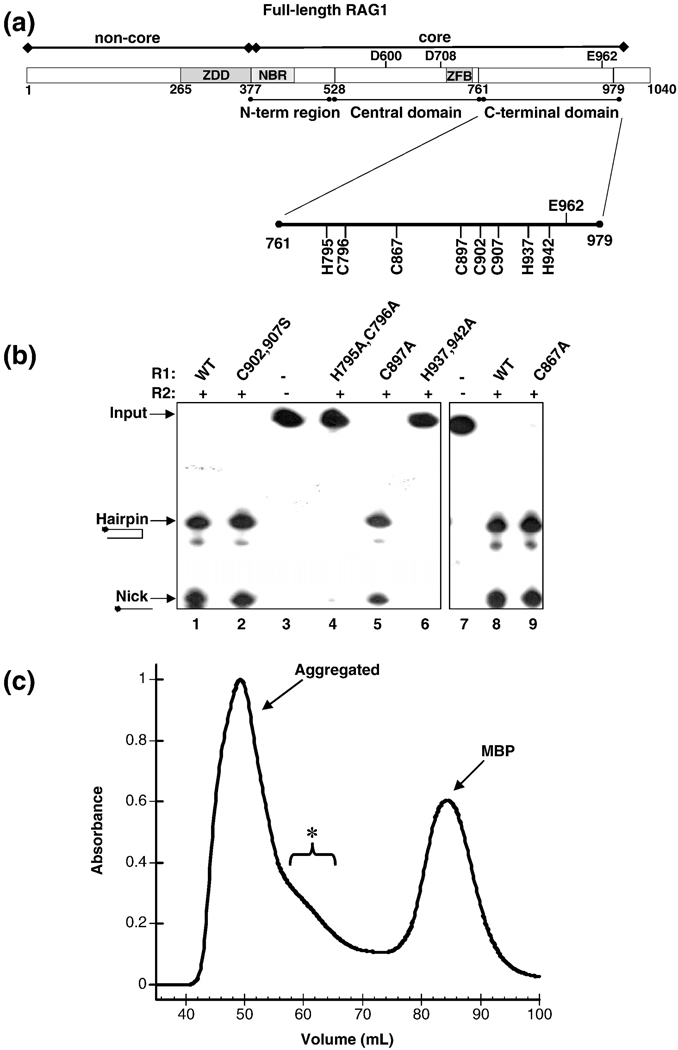
Figure 4.
(A) Domains in core RAG1. The core region is the minimal region required for catalysis. This region contains the nonamer binding region (NBR), a C2H2 zinc finger (ZFB) and the three active site residues (Asp-600, Asp-708 and Glu-962). The location of the central and C-terminal domains are shown below the bar representing core RAG1. (B) The effect of mutating conserved CTD His and Cys residues in mR1(core) on DNA cleavage activity. Analysis of coupled cleavage activity in buffer containing Mg2+. mR1(core) (0.04 µM) and gR2(core) (0.04 µM) proteins were incubated with HMGB1 (0.34 µM) and radiolabeled ds 12-RSS in the presence or absence of unlabeled ds 23-RSS. Lane 1 has no protein in the reaction, only ds 12-RSS. The ds 12-RSS substrate (input) and the nick and hairpin cleavage products are indicated. Also, the mR1(core) protein used in each sample (WT or mutant) is labeled above each lane. H795,C796A mR1(core) and H937,942A mR1(core) showed 0% nicking and hairpin formation. The activity of C902,907S mR1(core), C897A mR1(core), and C867A mR1(core) were approximately equal to the activity level of WT mR1(core). (C) Size exclusion chromatography profile of the C902A,C907A,H942A mR1(core) triple mutant from a preparative 120 ml Superdex 200 column. The chromatography was performed as described in Figure 3A for the WT mR1(core) sample purified in Zn2+-containing buffers. The bracket labeled with an asterisk denotes a shoulder on the aggregated peak that likely contains a mixture of oligomeric forms of the triple mutant.