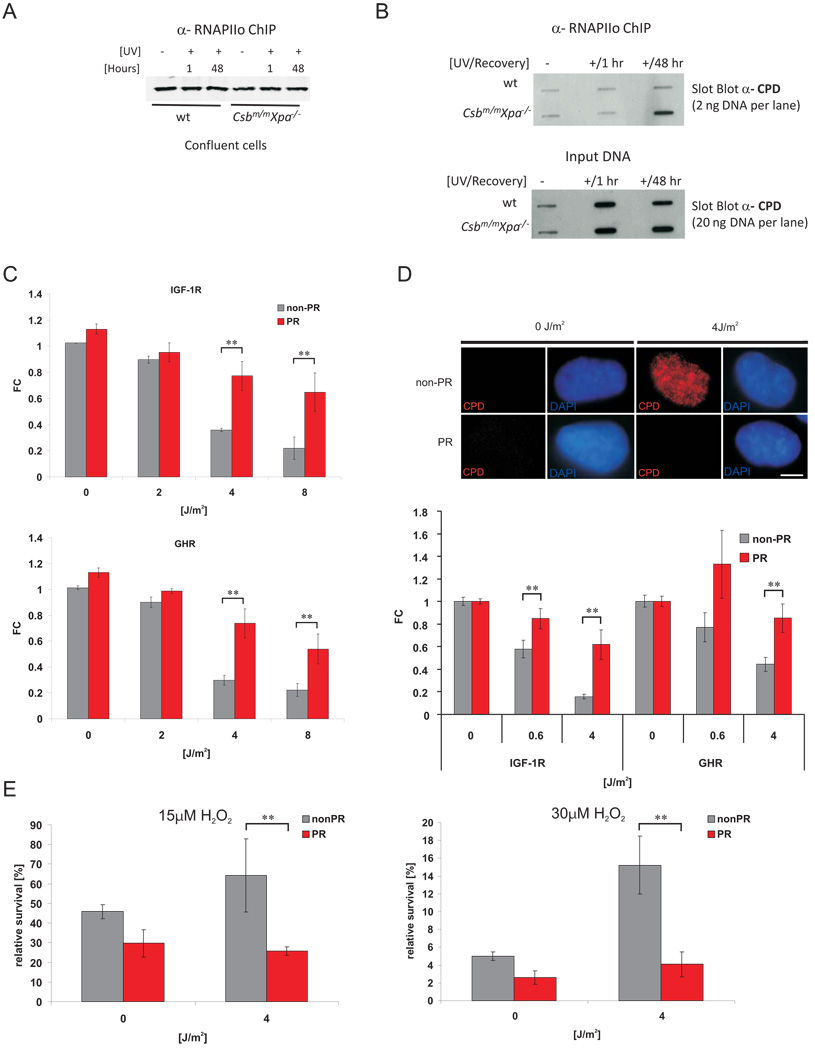
Figure 7. Repair of persistent CPD lesions alleviates IGF-1R and GHR repression and oxidative stress resistance.
A) RNAPIIo protein levels in RNAPIIo specific ChIP using chromatin of crosslinked UV- and non-irradiated confluent chondrocytes (as indicated). B) Slot blot analysis of different amounts of RNAPIIo co-ChIPed DNA (top panel) and input crosslinked DNA (lower panel) spotted at the same membrane using a CPD specific antibody (representative experiment shown). CPD and 6-4PP photolyase transgenic MEFs (C) or a CPD photolyase transgenic CS1AN human CS cell line (D) were UV treated and then either photoreactivated (PR) for 1h or kept in the dark (non-PR). IGF-1R and GHR expression levels were determined 6h post treatment and normalized to Gapdh, gTUB and Hprt. Removal of CPDs was assessed with an anti-CPD antibody (D, upper panel; scale bar 10µm) showing presence of CPDs in CSB cells and complete CPD repair after PR (6h post treatment, 1h PR). E) CS1AN cells carrying a CPD-photolyase trangene were treated with UV and either for 1h PR or left in the dark. 12h post UV exposure cells were treated with indicated doses of hydrogen peroxide. Relative survival was determined by comparing cell numbers after 72h to non-H2O2 treated controls (FC = fold change compared to untreated controls; *=p<0.05, **=p<0.01, two-tailed t-test, error bars = SD, n=4).