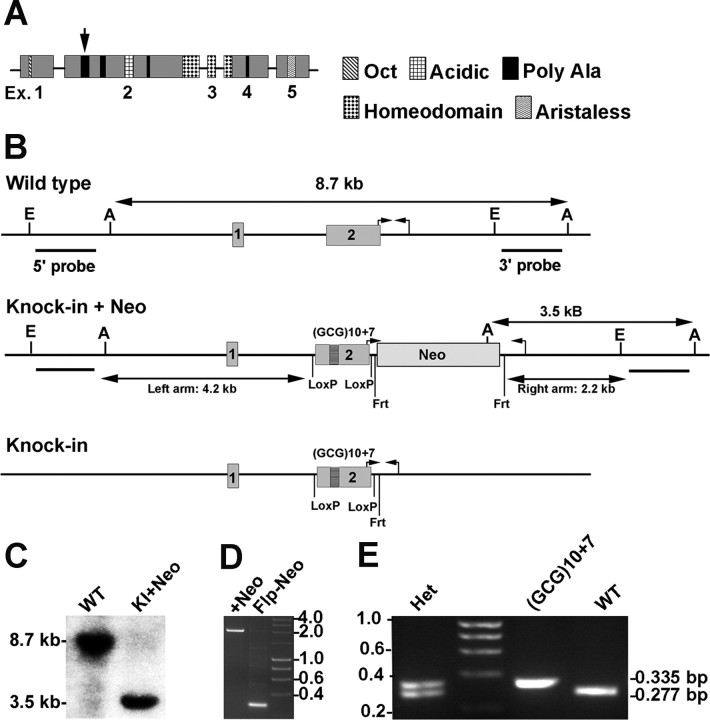
Figure 1.
Structure of the ARX protein and gene, and generation of Arx(GCG)10+7 mice. A, Schematic model of the 564 residue ARX protein showing the exon structure, position, and relative size of known protein domains and the four polyalanine tracts [tract 1 is indicated (arrow)]. B, Schematics of exon 1- and 2-containing (1, 2) region of the Arx gene at Xp21.3 relevant to the (GCG)10+7 knock-in into polyalanine tract 1. The long arrows show the AseI-based Southern blot strategy using a 3′-probe distinguishing wild-type embryonic stem cells from those with the entire knock-in construct recombined (Knock-in + Neo) (C). A second strategy with the 5′-probe used EcoRI fragments (E to E). Probe bars represent 1 kb. The small arrow pairs indicate where diagnostic PCR primers anneal. The knock-in plus Neo schematic demonstrates the left and right homologous arms in the targeting construct, loxP sites flanking the (GCG)10+7 knock-in into polyalanine tract 1, and the frt-flanked neomycin-resistance cassette. The knock-in schematic illustrates the remaining sequence in targeted embryonic stem cells after flp recombinase removed the neomycin-resistance cassette. C, Southern blot of AseI-digested genomic DNA from embryonic stem cells that are WT or contain the knock-in plus neomycin-resistance cassette (KI+Neo), labeled with the 3′-probe. D, Gel of the 2 kb versus 0.335 kb PCR products (small hooked arrow pairs in schematics) from targeted stem cells before (+Neo) and after (Flp-Neo) Flp-recombinase removed the neomycin-resistance cassette. The latter cells were used to produce the chimeras founding the Arx(GCG)10+7 lines. Molecular weight markers are indicated. E, Gel with the three possible genotyping PCR products. Female heterozygotes show both WT 0.277 kb and 0.335 kb (GCG)10+7 bands. Male hemizygous or female homozygous (GCG)10+7 show a 0.335 kb band (small hooked arrow pairs in B). Molecular weight markers are in 0.2 kb increments.