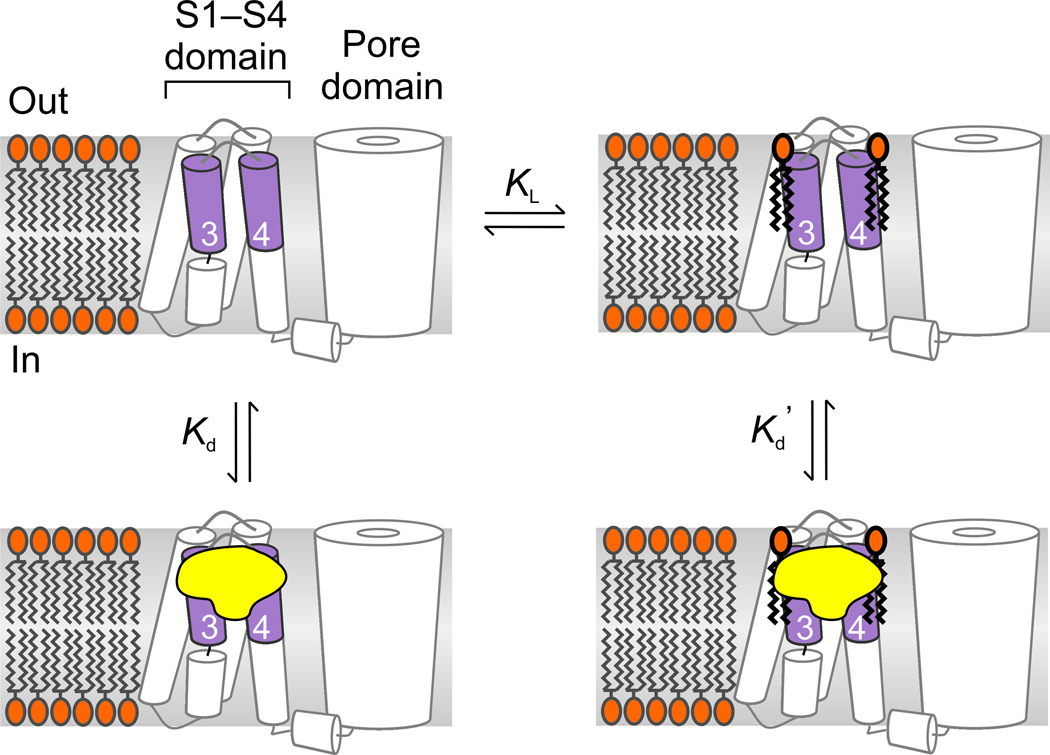
Figure 5.
Model illustrating toxin binding to lipid-associated paddle motifs. Lipids are depicted as binding and unbinding from the paddle motif and toxin affinity is higher for paddle motifs with lipids bound (Kd’<Kd). Conversion of sphingomyelin to ceramide-1-phosphate could enhance toxin affinity either because the modified lipid binds more strongly (lower KL) or because the toxin binds tighter to paddles interacting with ceramide-1-phosphate compared to sphingomyelin.