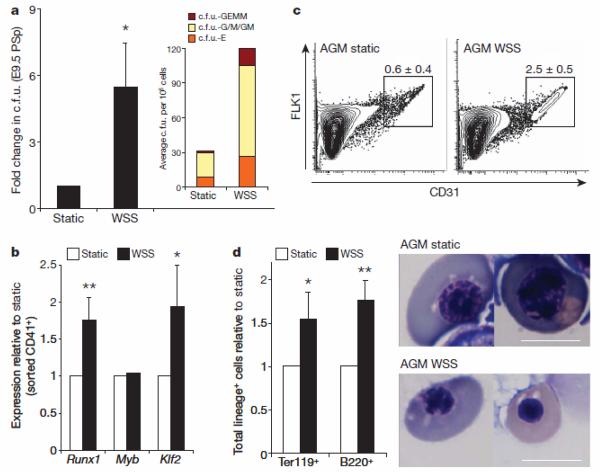
Figure 3. Shear stress induces haematopoiesis in PSp/AGM-embryo-derived cells.
a, Methylcellulose haematopoietic c.f.u. assay. WSS increases the frequency of haematopoietic progenitors in two-dimensional primary PSp cultures from E9.5 embryos; n = 4(P = 0.038); bar graphs represent average ± s.e.m. Inset shows average distribution of haematopoietic colony types. b, WSS induces upregulation of the haematopoietic markers Runx1 (P = 0.01) and Klf2 (P = 0.05) in FACS-sorted AGM-derived CD41+ haematopoietic progenitors as documented by real-time PCR; n = 3, bar graphs represent average ± s.e.m. c, FACS analysis. WSS induces an increase in CD31+ cells in two-dimensional primary AGM cultures; P = 0.005, n = 3, average ± s.d. d, WSS modulates the differentiation of AGM-derived haematopoietic progenitors as shown by an increase in absolute number of cells positive for the erythroid marker Ter119 (P = 0.02) and for the lymphoid marker B220 (P = 0.01); n = 3, bar graphs represent average ± s.e.m. Shear stress induces maturation of erythroid precursors as documented by cell morphology in cytospins, which show pycnotic erythroblasts in WSS-treated samples, and polychromatic erythroblasts in static cultures. Scale bar, 10 μm. *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.