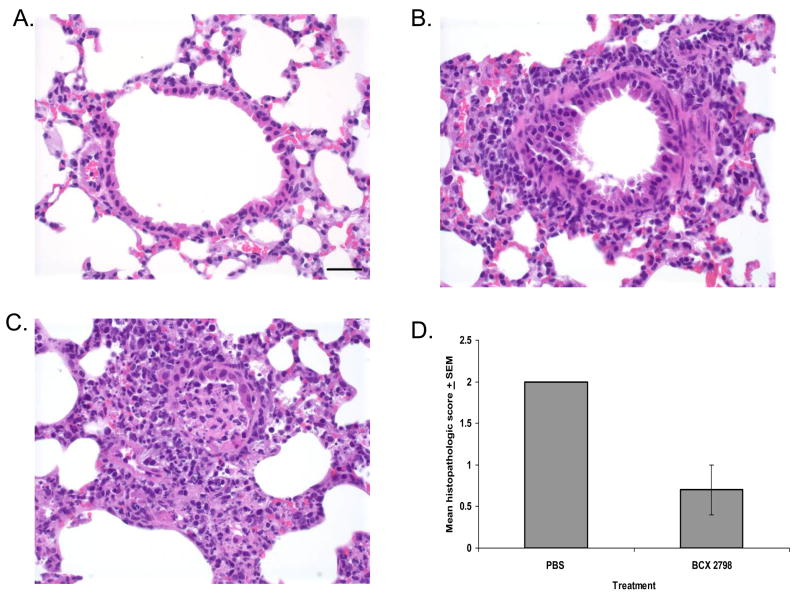
FIG. 4.
Effect of treatment with BCX 2798 on histopathologic changes in lungs of mice infected with 100 PFU of rSeV(hPIV-1HN). Infected mice (three per group) were intranasally treated with 10 mg/kg/d of compound or PBS for 5 d starting 24 h after infection. Lungs were removed 8 d after infection. The sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and examined microscopically. High-power view (400×) of the stained section is shown. Bar = 30 μm. (A) Uninfected mice treated with PBS; (B) Infected mice treated with BCX 2798 (note the mild peribronchiolar infiltrates of lymphocytes, plasma cells and neutrophils and absence of airway epithelial necrosis); (C) Infected mice treated with PBS (note a peribronchiolar cuffing of the distal airway by inflammatory cells; the airway lumen is plugged by a mixture of sloughed necrotic epithelial cells and inflammatory cells, and there is local extension of the inflammation and necrosis into the alveoli); (D) Histopathologic scoring of infected mouse lungs. The degree of histopathologic changes was graded on a scale of 0 (no change) to 4 (severe pneumonia). The averages for each group are plotted with error bars indicating the SEM.