FIG. 1.
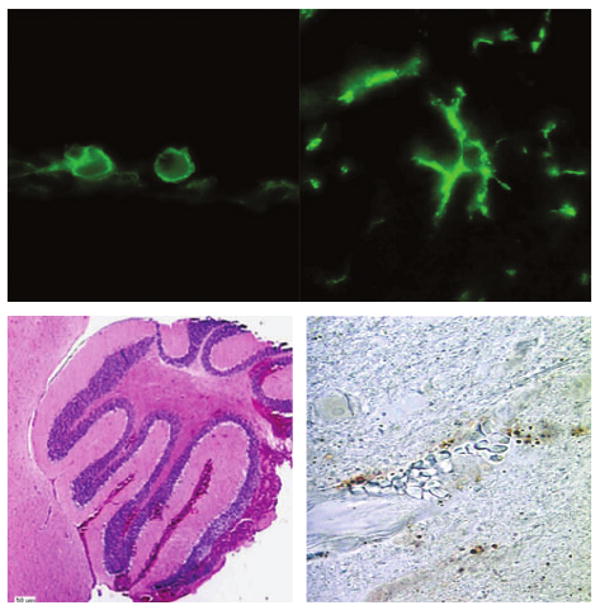
Spectrum of brain pathology in relapsing fever (RF). Infection with the RF spirochaete Borrelia turicatae can result in prominent changes in the brain parenchyma that vary from macrophage infiltration/microglial activation (top panels, ×1000 magnification) of varying degrees in wild-type and B-cell-deficient mice to severe intracerebral haemorrhage (left lower panel) with prominent brain microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis (right lower panel) in RAG2-deficient mice infected with serotype 2. The upper panels show immunofluorescence staining with rat monoclonal antibody anti-mouse F4/80. The left lower panel shows haematoxylin and eosin staining of the cerebellum, and the right lower panel shows terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labelling staining of the cerebral cortex.
