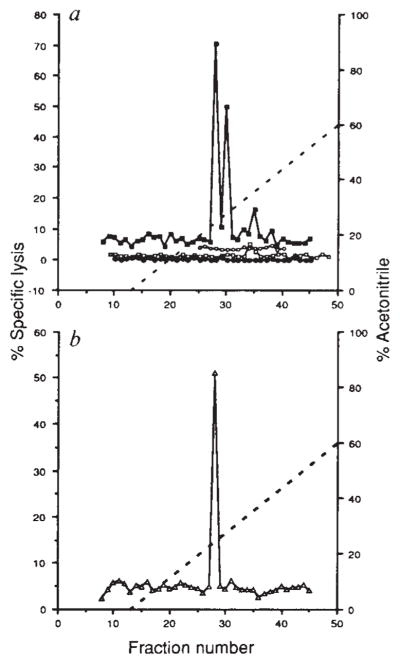
FIG. 2.
Recognition by CTL line LmT and clone B9 of natural peptides derived from L. monocytogenes by acid extraction of infected spleens, a, CTL line LmT was used to lyse 51Cr-labelled P815 cells coated with reversed-phase HPLC fractions of acid extracts from infected BALB/c (■) and C57BL/6 (○) spleens and uninfected BALB/c (□) spleens. EL4 cells were also used with HPLC fractions from infected BALB/c spleens (●). Effector to target ratio was 20:1. b, CTL clone B9 was assayed on P815 cells coated with HPLC fractions of acid extracts from infected BALB/c spleens (△). Effector to target ratio was 20:1.
METHODS. BALB/c mice were infected with 5×105 L. monocytogenes and C57BL/6 mice were infected with 106 L. monocytogenes. After 48 h the spleens were taken and homogenized sequentially with a tissue grinder and dounce homogenizer in 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) and sonicated as described24. This material was centrifuged at 100,000g for 30 min and the supernatant was passed over a Sephadex G-25 column. Material of less than 5K was collected and lyophilized. HPLC of the acid extract from one spleen in 0.1% TFA was performed with a C18 300A reversed-phase column using a 0–60% gradient of acetonitrile with 0.1% TFA at a rate of 1 ml min−1 and 1 ml fractions were collected. Fractions were lyophilized and suspended in 100 μl PBS. CTL assays were performed for 4 h with LmT and B9 effectors using either P815 or EL4 target cells in 200-μ1 wells, of which 50 μl represented the HPLC fraction.