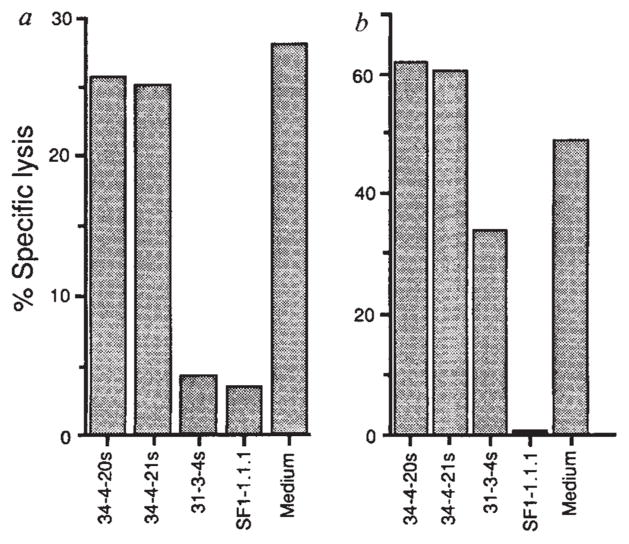
FIG. 3.
Presentation of HPLC Fraction 28 by H-2Kd and lysis of P815 cells transfected with LLO. a, P815 cells were coated with HPLC fraction 28 peptides and exposed to LmT CTL in the presence of monoclonal antibodies 34-4-20s and 34-4-21s, which are specific for H-2Da, and 31-3-4s25 and SF1-1.1.1, which are specific for H-2Kd. b, P815 cells transfected with LLO (PHem3) were used as targets for LmT CTL in the presence and absence of anti-H-2d antibodies as in a.
METHODS. P815 and PHem3 cells were labelled with 51Cr and suspended in culture supernatants from hybridomas 34-4-20s, 34-4-21s, 31-3-4s, SF1-1.1.1 and control medium. Fraction 28 peptides were added to the P815 targets. LmT effectors were added to targets at a ratio of 20:1 and the specific lysis was determined after 3 h. PHem3 was obtained by transfecting P815 cells with linearized pHβAPr-1-neo26 containing the entire LLO gene17. Bases 1-1,587 of the hlyA gene encoding LLO were cloned into the BamHI site of the pHβAPr-1-neo expression vector after polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification from L. monocytogenes DNA. The oligonucleotides used for priming were 5′-CCCGGGATCCACCATGAAAAAAATAATGCTAG-3′ and 5′-GGATCCGGATCCTTATTCGATTGGATTATC-3′ which introduced flanking BamHI sites. Electroporation of PvuI linearized plasmid containing the insert into P815 cells and selection of G418 resistant clones was performed as described23. P815 cells transfected with the vector without the insert were not lysed by the LmT CTL line (not shown).