Figure 1.
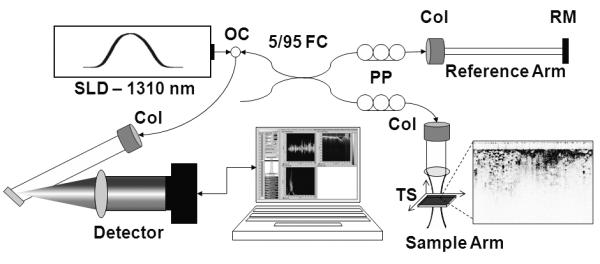
Clinical spectral-domain optical coherence tomography system schematic. Light from a SLD (λ=1310 nm) is directed into an optical circulator (OC) and to a fiber coupler (FC) which splits 5% of the light to a reference arm mirror (RM) and 95% of the light to a sample arm containing focusing optics and an automated x-y translation stage (TS). Light is collimated through fiber collimators (Col). Reflected light from each arm is coupled through polarization paddles (PP), interfered within the fiber coupler, and spectrally dispersed onto a line camera.
