Table 2.
SAR and ADME profiles of follow-up compounds of lead TNAP inhibitor 1
| CMPD | TNAP IC50 μM luminescenta |
Microsomal/ Plasma Stabilityb |
PAMPA (% FLUX)c |
Solubility (μg/mL)d |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 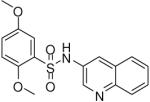 |
0.19 (0.03, 0.41, 43) | 78 / 97 | 58 | 138.2 |
| 18 | 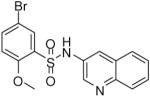 |
0.12 (0.04, 0.25, 16) | 49 / 66 | 54 | 37.9 |
| 19 | 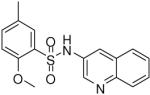 |
0.65 (0.50, 0.94, 4) | 48 / 91 | 7 | 71.6 |
| 20 | 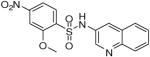 |
0.74 (0.74, 0.74, 1) | 56 / 96 | 11 | 178 |
| 21 | 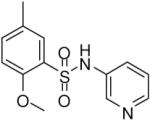 |
1.85 (0.69, 3.36, 23) | 39 / 98 | 83 | 28.5 |
| 22 | 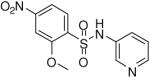 |
3.16 (2.27, 3.64, 4) | 68 / 99 | 51 | 1.1 |
TNAP IC50 data are presented as the geometric mean followed in parentheses by the lower and upper limits of the mean and the number of replicates.
Percent remaining after incubation for 30 min. at 37 °C.
PAMPA flux values assessed according to previously published methods.15
Solubility measurements performed in an aqueous buffer solution at pH 7.4, in duplicate.
