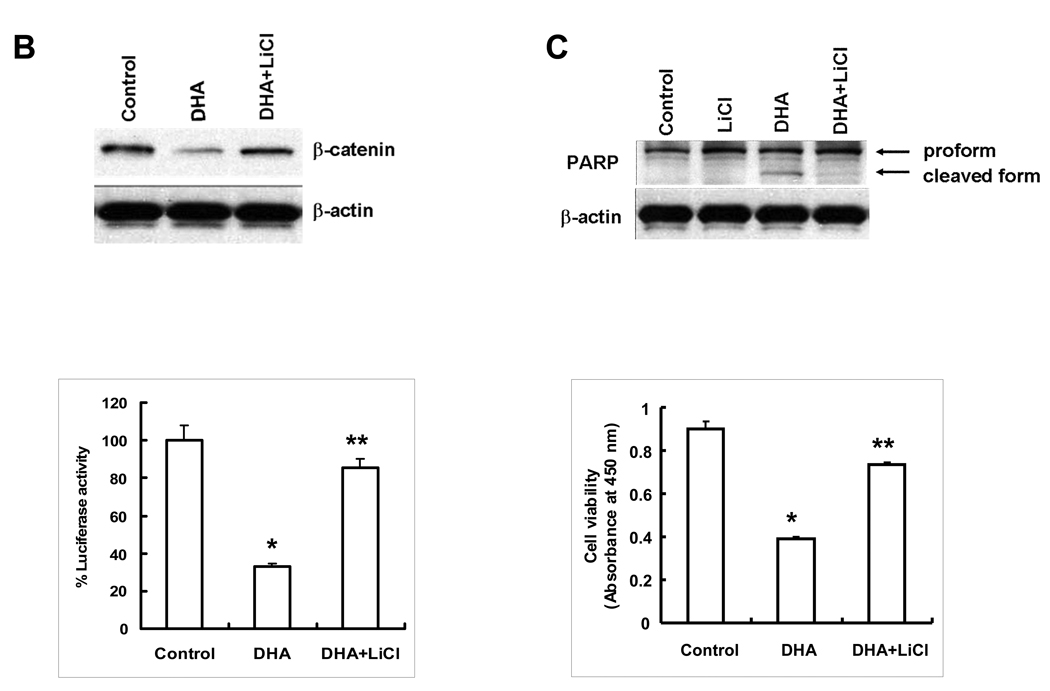
Figure 3. ω-3 PUFAs inhibit GSK-3β phosphorylation in HCC cells.
(A) Hep3B cells were treated with 60 µM of DHA, EPA or AA in serum free medium for indicated time periods. The cell lysates were obtained for Western blot analysis using antibodies against p-GSK-3β and GSK-3β as well as p-Akt as described in Materials and Methods. DHA or EPA treatment resulted in p-GSK-3β dephosphorylation, whereas AA had no effect. (B) Inhibition of GSK-3β by LiCl prevents DHA-induced β-catenin degradation. (Upper Panel) Hep3B cells were pretreated with LiCl (20 mM) for 1 hr before DHA treatment (20 µM) for 24 hr; the cell lysates were obtained for Western blot analysis using the antibody against β-catenin. (Lower Panel) Inhibition of GSK-3β by LiCl prevents DHA-mediated reduction of TCF/LEF reporter activity. Hep3B cells transfected with the TCF/LEF reporter construct were treated with LiCl (20 mM) for 1 hr followed by DHA treatment (20 µM) for 24 hr. The cell lysates were obtained to determine the luciferase activity. The data are presented as mean ± SD of six independent experiments (*p<0.01 compared to control; **p<0.01 compared to DHA treatment). (C) LiCl prevents DHA-induced PARP cleavage and cell viability. (Upper Panel) Hep3B cells were pretreated with LiCl (20 mM) for 1 hr followed by DHA treatment (20 µM) for 24 hr. The cell lysates were obtained for Western blot analysis using the antibody against PARP. (Lower Panel) LiCl restores DHA-induced cell death. Hep3B cells pretreated with LiCl (20 mM) for 1 hr were incubated with DHA for 24 hr. The cell growth was determined using WST-1 assay. The data are presented as mean ± SD of six independent experiments (*p<0.01 compared to control; **p<0.01 compared to DHA treatment). EPA was not utilized for LiCl experiments.