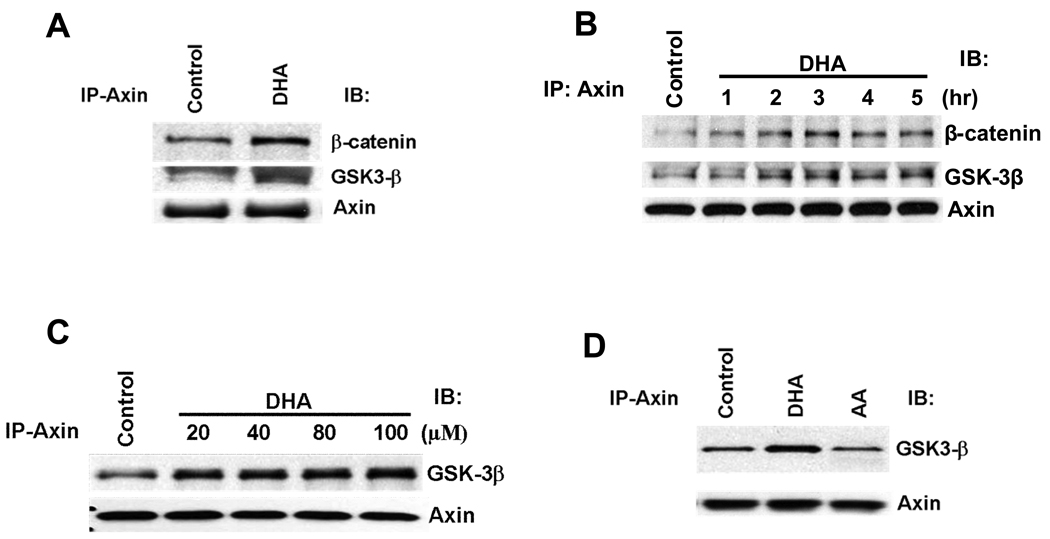
Figure 4. DHA induces the formation of Axin/GSK-3β/β-catenin complex in HCC cells.
(A) The effect of DHA on the association of Axin with β-catenin and GSK-3β. Hep3B cells were treated with DHA (60 µM) for 1 hr. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitaed with anti-Axin antibody followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against GSK-3β, β-catenin, and Axin. (B) The time course effect of DHA. Hep3B cells were treated with DHA (60 µM) at different time points (1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 hours). The cell lysates were immunoprecipitaed with anti-Axin antibody followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against GSK-3β, β-catenin, and Axin. (C) The dose-dependent effect of DHA. Hep3B cells were treated with different concentration of DHA for 1hr. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitaed with anti-Axin antibody followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against GSK-3β and Axin. (D) AA did not alter Axin and GSK-3β association. Hep3B cells were treated with 60 µM AA, DHA or vehicle for 1 hr. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitaed with anti-Axin antibody followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against GSK-3β and Axin. EPA was not utilized in these experiments.