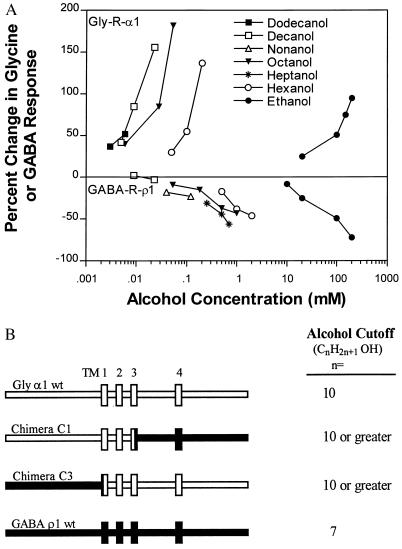
Figure 1.
(A) Determination of alcohol cutoff in homomeric Gly-R-α1 (Upper) and GABA-R-ρ1 (Lower) expressed in Xenopus oocytes. The n-alcohols potentiate Gly-R-α1 and inhibit GABA-R-ρ1 function. The alcohol cutoffs differ between the two receptors: Gly-R-α1 has a cutoff of decanol and GABA-R-ρ1 has a cutoff of heptanol. (Upper) Data are adapted from Mascia et al. (13) and were gathered from 5 to 8 oocytes. (Lower) Data are adapted from Mihic and Harris (15) and were gathered from 3 to 11 oocytes, except for data on the effects of decanol on the GABA-R-ρ1, which were determined from 4 oocytes in the present study. Error bars are omitted for clarity; in each case, the SEM for each point was typically less than 10% of the mean. (B) n-Alcohol cutoffs of wild-type Gly-R-α1, GABA-R-ρ1, and C1 and C3 chimeric receptors. Schematic representations of the receptors are shown on the left; the four transmembrane domains are depicted as vertically oriented rectangles. Gly-R-α1 sequences are open; GABA-R-ρ1 sequences are solid. Interfaces between open and solid bars indicate chimera junction sites. For chimera C1, the junction site is immediately after Gly-R-α1 E300; for chimera C3, the junction site is after GABA-R-ρ1 Val-274 (numbering is based on the amino acid sequence after signal peptide cleavage). The n-alcohol cutoffs of the wild-type receptors (Gly-R-α1 and GABA-R-ρ1) were determined from A. The n-alcohol cutoff of chimera C1 was estimated to be 10 or greater because of the similar increase in potency in the n-alcohol series ethanol, hexanol, and decanol for both chimera C1 and the Gly-R-α1. The n-alcohol cutoff of chimera C3 was based on analysis of the effects of ethanol, hexanol, octanol, decanol, and dodecanol, all of which exhibited increased potency over the previous alcohol. All of the receptors were expressed in Xenopus oocytes and tested with an EC5–10 concentration of GABA or glycine.