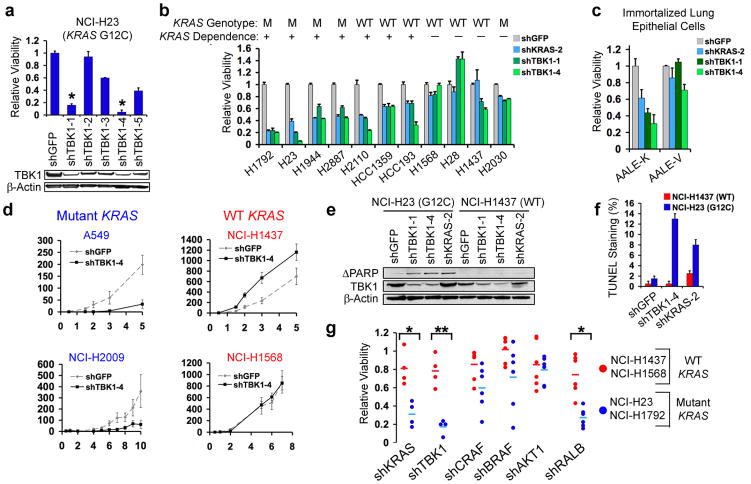
Fig. 2.
TBK1 synthetic lethality with oncogenic KRAS. (a) Top-scoring TBK1-specific shRNAs (*) induced lethality and TBK1 suppression (immunoblot) in NCI-H23 cells (mutant KRAS). (b) Suppression of KRAS or TBK1 in NSCLC cell lines. HCC-1359 and HCC-193 cells expressed RAS and NF-κB signatures. (c) KRAS and TBK1 dependence of lung epithelial cells expressing oncogenic KRAS (AALE-K) or vector (AALE-V). (d) Tumor formation following TBK1 suppression. Mean and SEM of at least 11 replicates shown. (e) Immunoblot of cleaved PARP following TBK1 or KRAS suppression. (f) Percentage of TUNEL positive nuclei following TBK1 or KRAS suppression. Mean and SD shown. (g) Differential cell viability following KRAS, TBK1, CRAF, BRAF, AKT1 or RALB suppression in KRAS mutant vs. WT cell lines (t-test for comparisons). SEM of triplicate samples normalized to shGFP control vector shown.