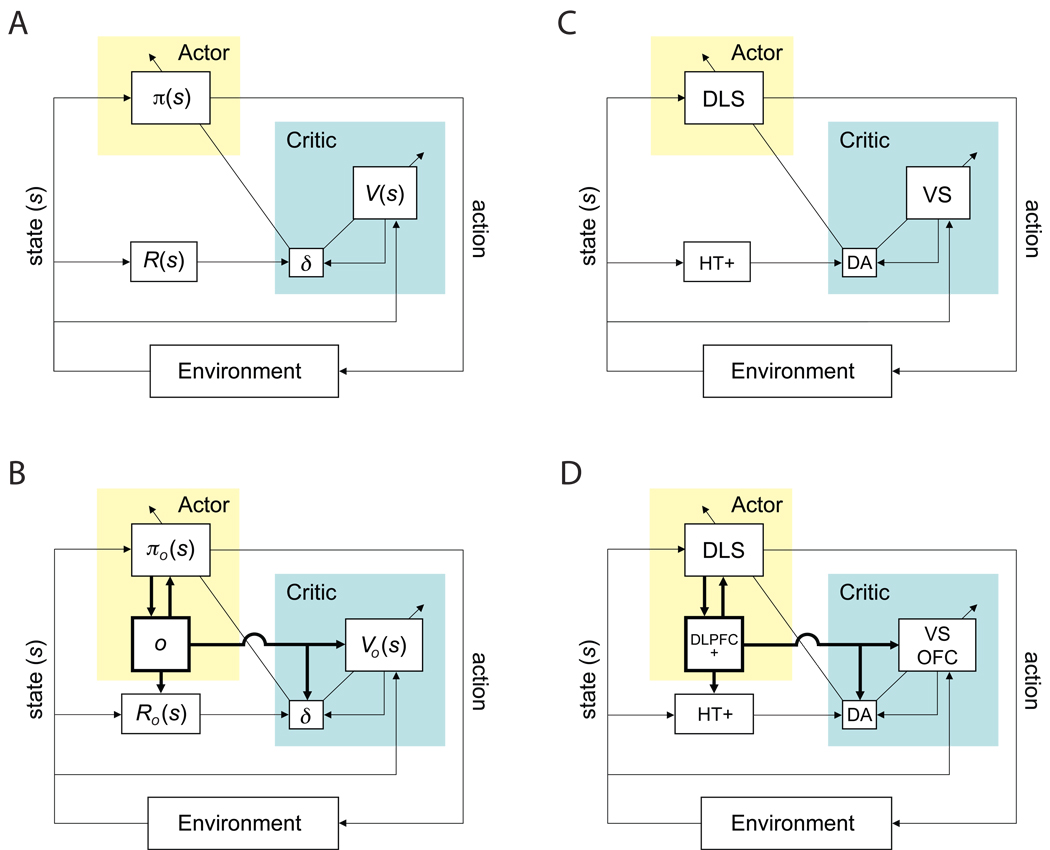
Figure 2.
An actor-critic implementation. (A) Schematic of the basic actor-critic architecture. R(s): reward function; V(s): value function; δ: temporal difference prediction error; π(s): policy, determined by action strengths W. (B) An actor critic implementation of HRL. o: currently controlling option, Ro(s): option-dependent reward function. Vo(s): option-specific value functions; δ: temporal difference prediction error; πo(s): option-specific policies, determined by option-specific action/option strengths. (C) Putative neural correlates to components of the elements diagramed in panel A. (D) Potential neural correlates to components of the elements diagramed in panel C. Abbreviations: DA: dopamine; DLPFC: dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, plus other frontal structures potentially including premotor, supplementary motor and pre-supplementary motor cortices; DLS, dorsolateral striatum; HT+: hypothalamus and other structures, potentially including the habenula, the pedunculopontine nucleus, and the superior colliculus; OFC: orbitofrontal cortex; VS, ventral striatum.