Table 3.
In Situ Trapping with Aldehydes and Ketonesa
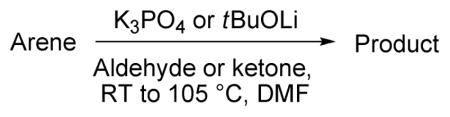 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| reagent | ||||
| entry | arene | base | product | yield |
| 1 | 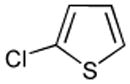 |
Ph2CO tBuOLi |
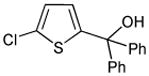 |
41% |
| 2 | 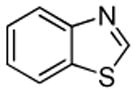 |
Ph2CO tBuOLi |
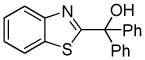 |
77% |
| 3 | 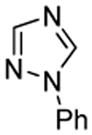 |
tBuCHO tBuOLi |
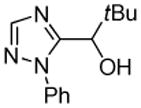 |
66% |
| 4 | 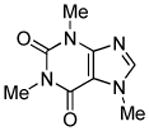 |
tBuCHO tBuOLi |
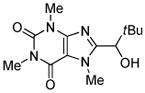 |
91% |
| 5 | 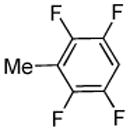 |
tBuCHO tBuOLi |
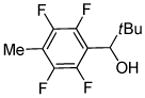 |
68% |
| 6 | 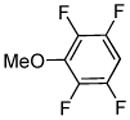 |
p-Chloro-benzaldehyde tBuOLi |
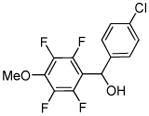 |
93% |
| 7 | 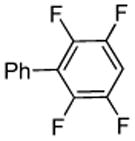 |
p-Chloro-benzaldehyde tBuOLi |
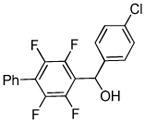 |
85% |
| 8 | 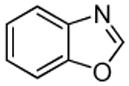 |
C6H11CHO K3PO4 |
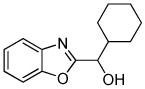 |
50% |
Substrate (1 equiv), base (1.5–3.0 equiv), ketone or aldehyde (3.0 equiv). Yields are isolated yields. See the Supporting Information for details.
