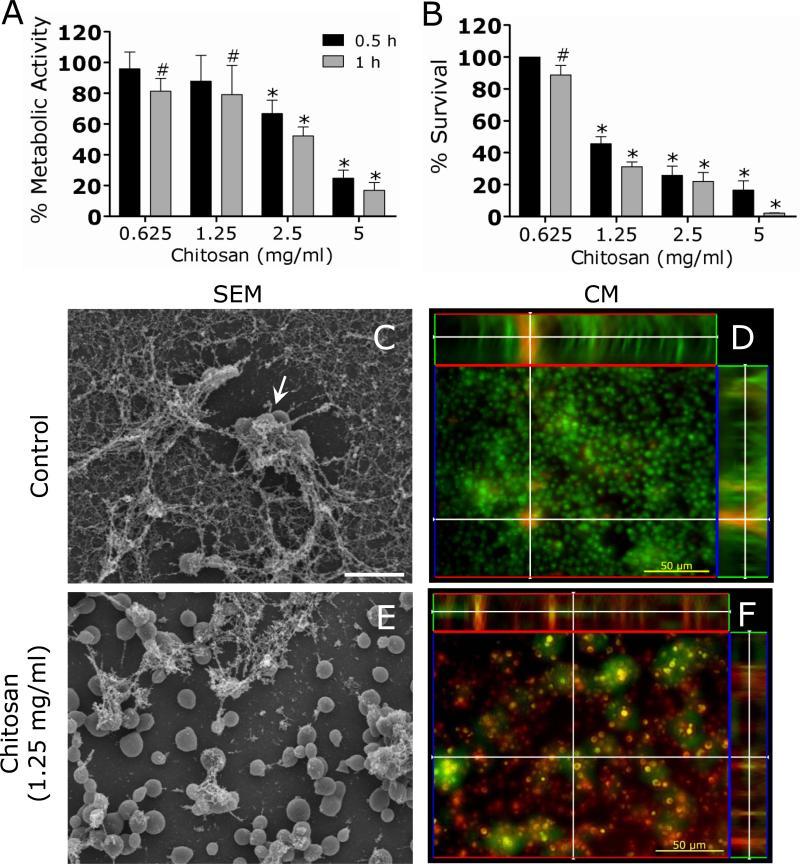
Figure 3. C. neoformans biofilms are susceptible to chitosan.
(A) The percentage of metabolic activity of untreated and chitosan-treated C. neoformans strain B3501 biofilms was measured by the XTT reduction assay. (B) The percent survival of untreated and chitosan-treated C. neoformans strain B3501 biofilms was measured by determination of the numbers of CFU. For A and B, Biofilms were exposed to 1.25 mg/mL of chitosan for 0.5, and 1 h; and their metabolic activities were compared to those biofilms incubated in PBS. The bars are the averages of four measurements, and brackets denote standard deviations. #, P<0.05 and *, P<0.001 in comparing the untreated and chitosan-treating groups. These experiments were done twice, with similar results each time. (C and E) SEM of C. neoformans B3501 biofilms (C) untreated and (E) treated with chitosan. Biofilms grown in the presence of 1.25 mg/mL of chitosan showed fungal cells (white arrow) surrounded by large amounts of exopolymeric matrix. In contrast, biofilms co-incubated with chitosan displayed yeast cells lacking capsular and released polysaccharide. Scale bar for C and E: 10 μm. (D and F) CM of C. neoformans B3501 biofilms (D) untreated and (F) treated with chitosan. Orthogonal images of mature C. neoformans biofilms showed metabolically active (red, FUN-1-stained) cells embedded in the polysaccharide extracellular material (green, MAb 18B7-FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG1 stained), while the yellow-brownish areas represent metabolically inactive or nonviable cells. Images were obtained after 1 h of exposure of the fungal cells to 1.25 mg/mL of chitosan, and the images were compared with those of biofilms incubated in presence of PBS. The pictures were taken by using x40 power field. Scale bars: 50 μm. The results are representative of those of two experiments.