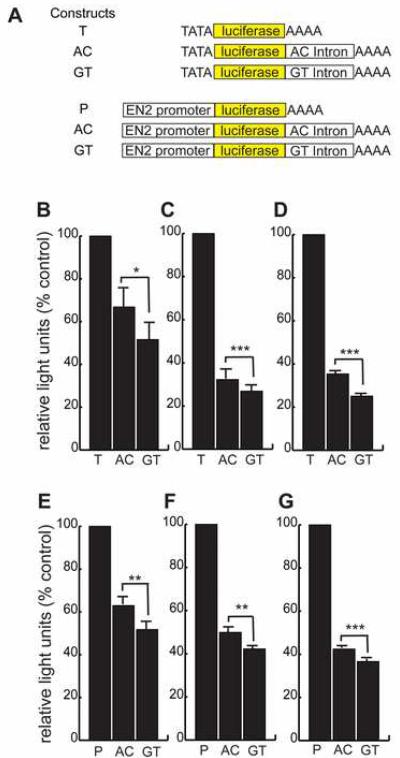
Figure 2.
Functional difference between rs1861972-rs1861973 A-C and G-T haplotypes. (a) The functional difference between the A-C and G-T intronic haplotypes was investigated by generating the diagrammed luc reporter constructs: T- SV40 minimal promoter 5' of luc without EN2 intron, P- EN2 promoter (-1 to -5735) 5' of luc without EN2 intron, AC- EN2 intron with rs1861972-rs1861973 A-C haplotype cloned 3' of luciferase but 5' of the SV40 polyadenylation signal to approximate the endogenous locus, GT- EN2 intron with rs1861972-rs1861973 G-T haplotype cloned 3' of luciferase but 5' of the SV40 polyadenylation signal. (b-d) Relative light units of luciferase normalized to Renilla reniformis and expressed as percent of control, pgl3 promoter vector (T), is shown for the SV40 minimal promoter constructs transiently transfected into (b) P6 cerebellar granule neurons (n=6), (c) PC12 cells (n=6) and (d) HEK293T cells (n=6). (e-g) Normalized relative light units of luciferase for luc EN2 promoter constructs expressed as percent of control (P) is shown for (e) P6 cerebellar granule neurons (n=7), (f) PC12 cells (n=6) and (g) HEK293T cells (n=6). * P<.005, ** P<.001, *** P < .00001, two tailed paired Student's T test