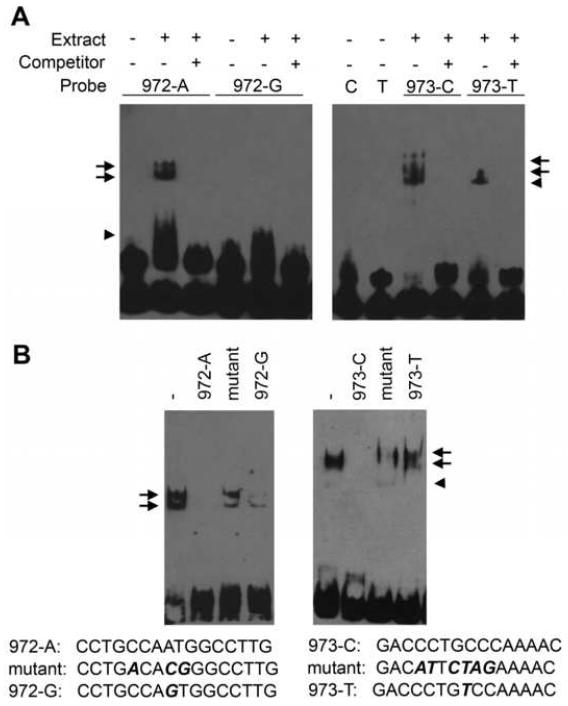
Figure 3.
Differential binding of nuclear proteins to rs1861972 and rs1861973 associated alleles. (A) To investigate whether the associated SNPs affect the binding of nuclear proteins, EMSAs were conducted with biotinylated 20-mer oligonucleotides and nuclear extract isolated from P6 mouse cerebellar granule cells. Extract was incubated with oligonucleotides specific to each allele, separated on a denaturing acrylamide gel, transferred to a membrane and detected by chemiluminescence. Several protein-DNA complexes were observed for both SNPs. Specificity was determined by competing with 100 molar excess of unlabelled oligonucleotide. Protein-DNA complexes specific to the associated rs1861972 A allele or rs1861973 C allele were observed (arrows) that were not detected for the corresponding rs1861972 G allele or rs1861973 T allele biotinylated oligonucleotides. In addition, protein-DNA complexes common to both alleles for rs1861972 or rs1861973 were observed (arrowheads). Abbreviations: 972-A: 20-mer oligonucleotide specific to the rs1861972 A allele, 972-G: 20-mer oligonucleotide specific to the rs1861972 G allele, 973-C and C: 20-mer oligonucleotide specific to the rs1861973 C allele, 973-T and T: 20-mer oligonucleotide specific to the rs1861973 T allele, + or -: presence or absence respectively of extract or 100 molar excess of unlabelled oligonucleotide. (B) To examine allele-specific binding of nuclear proteins to rs1861972 (left) and rs1861973 (right), additional competitions were performed. 80 molar excess of 3 different unlabelled oligonucleotides were each added individually to the probe and nuclear extract: oligonucleotide with the same sequence as the biotinylated probe (972-A, 973-C), mutant oligonucleotides predicted to disrupt NF1, NFY, C/EBP binding to the A allele of rs1861972 or Sp1 and Ets binding to the C allele of rs1861873, and oligonucleotides for the non-associated G (972-G) and T (973-T) alleles. The sequence for each oligonucleotide is shown. Abbreviation: - absence of competitor