Fig. 1.
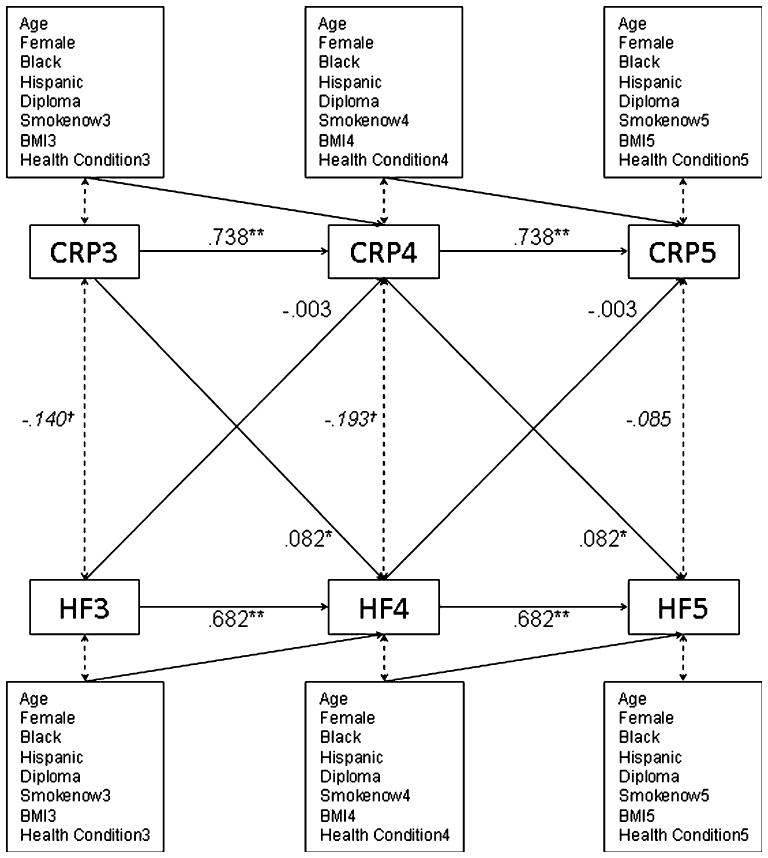
Cross-lagged panel model showing that CRP predicts increases in HF HRV over a 1-year period, but HF HRV does not predict changes in CRP. Regression weights are unstandardized. In addition to temporal stability of serum CRP and HF over years 3 through 5, results show that a higher CRP in 1 year is associated with a greater increase in HF in the subsequent year. CRP C-reactive protein, HF high-frequency heart rate variability, smokenow current smoker, BMI body mass index, health condition hypertension, diabetes or use of cardiovascular, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetes or sex hormone replacement medications. Numeric suffixes refer to the study year. Covariances (italicized) are standardized (i.e., equivalent to correlations); **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, †P < 0.1
