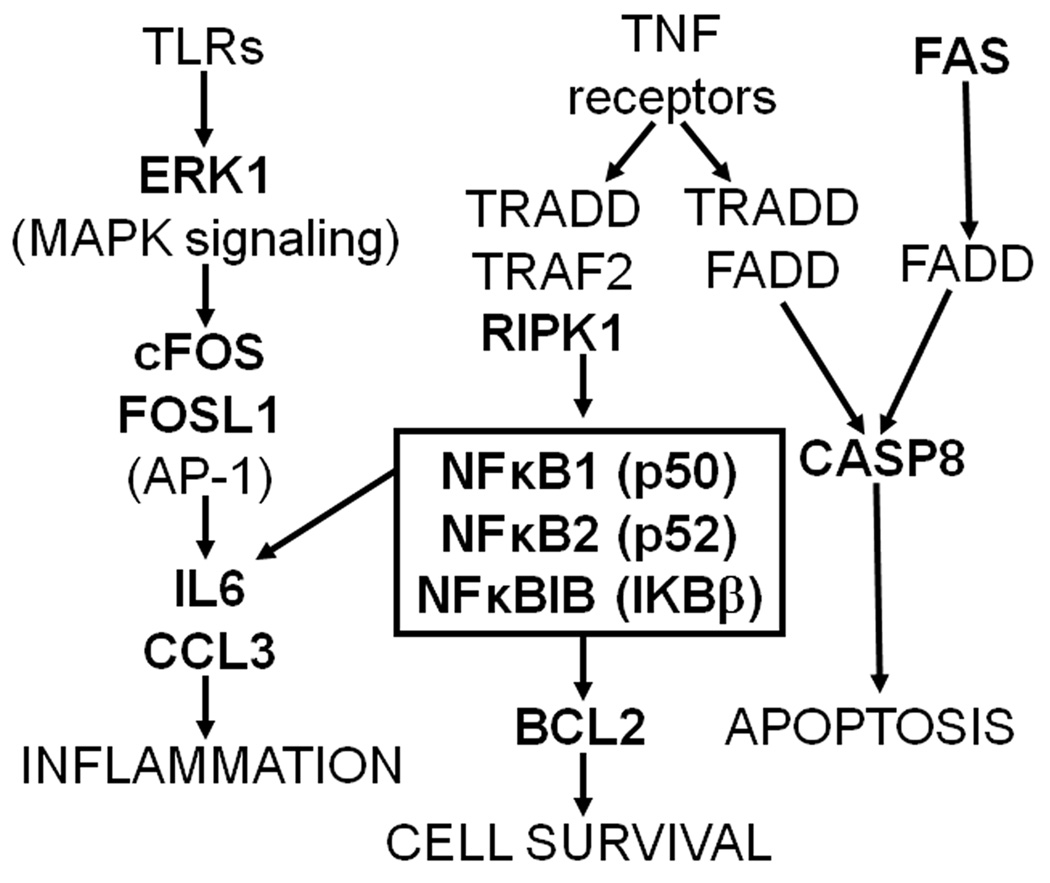
Figure 6. Gene pathways including genes that were differentially expressed following acute MA exposure (2 mg/kg) in MAHDR and MALDR selected line mice.
Fas, which was downregulated in response to MA in MALDR animals, is upstream of Casp8, a pro-apoptotic factor that was downregulated in response to MA in MAHDR animals. Ripk1, which was downregulated in MALDR mice, encodes a kinase that functions upstream of the NFκB transcription factor, components of which were differentially expressed in both selected lines. NFκB activates transcription of Bcl2, an anti-apoptotic factor which was downregulated in MALDR animals, and also activates transcription of various inflammatory peptides. Mapk3, which encodes the ERK1 kinase and functions downstream of Toll-like receptors to activate the AP-1 transcription factor, was downregulated in MAHDR animals. Two components of AP-1, cFos (upregulated in MAHDR) and Fosl1 (downregulated in MALDR) were also identified in our analysis. AP-1, like NFκB, activates transcription of inflammatory peptides, such as those encoded by Il6 (downregulated in MAHDR) and Ccl3 (downregulated in MALDR). These results suggest that changes in the function of signaling pathways involved in apoptosis and immune responses are partially responsible for the divergence in MA consumption behaviors in these selected lines.