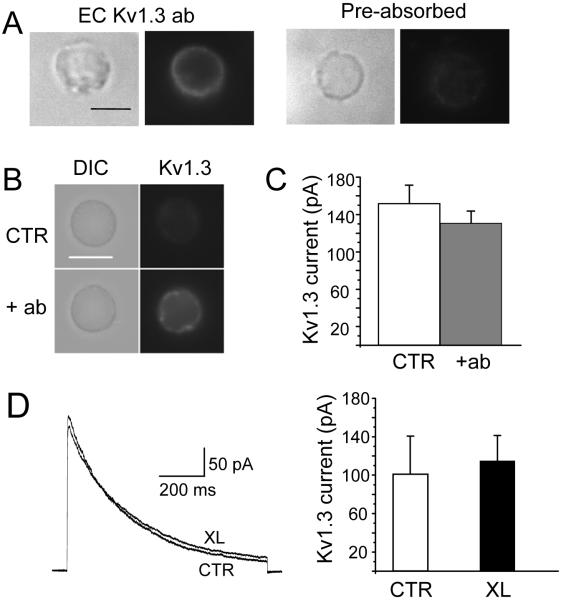
Figure 1.
Specificity and lack of functional effects of extracellular anti-Kv1.3 antibody (EC Kv1.3 ab). A. Human T cells were fixed and stained with EC-Kv1.3 antibody (left) or anti-Kv1.3 antibody pre-adsorbed to the antigen (right). The corresponding DIC and fluorescence micrographs for each set are shown. B-C. Jurkat T cells were incubated with EC-Kv 1.3 antibody at 1:1 and 100:1 ratio of antibody:Kv1.3 α subunit for 30 min at 37°C. After this time, cells were either patched or fixed and stained with secondary antibodies. The DIC and fluorescent images for Kv1.3 are shown for controls (no antibody) and cells treated with a 1:1 antibody:Kv1.3 α in panel B. For electrophysiological experiments, Kv1.3 currents were elicited by depolarizing voltages to +50 mV (-80 mV HP). The average Kv1.3 current for control (CTR, n=15) and T cell treated with a 100:1 antibody:Kv1.3 α (n=16) are reported in panel C. There was no difference between the two groups (p=0.18). The capacitance measured was similar in the two groups (8.6±0.4 pF for control and 8.1±0.5 pF for antibody-treated cells, p=0.25). D. Kv1.3 crosslinking does not affect the activity of Kv1.3. Kv1.3 currents were recorded in Jurkat T cells after Kv1.3 crosslinking (XL) and compared to control (CTR, no antibody) cells. Representative traces in CTR and XL cells are shown in the left panel. Currents were elicited by depolarizing voltage steps to +50 mV (-80 mV HP). The average current amplitudes for CTR (n=6) and XL (n=8) are reported in the right panel. There was no difference in capacitance among these groups (3.8±0.3 pF for CTR and 3.6±0.3 pF for XL).