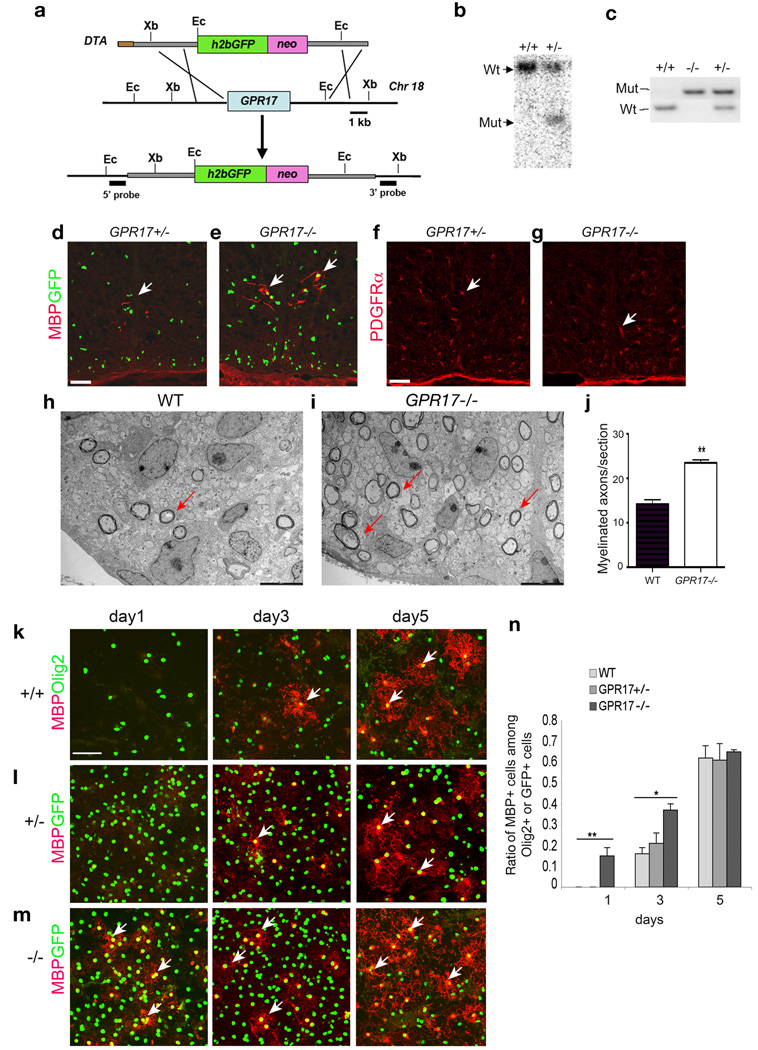
Figure 6. Early onset of oligodendrocyte myelination in GPR17 null mice.
a) Schematic strategy for disruption of GPR17 on the mouse chromosome 18. Abbreviations: h2bGFP, histone2b GFP; neo, the neomycin selection marker; and DTA, the diphtheria toxin gene. Ec: EcoRI, Xb: XbaI. b) Southern blot validation with a 5′ GPR17 probe identified the targeted locus as a following EcoRI digestion of genomic DNAs. c) PCR genotyping analysis of WT and targeted allele from WT, GPR17+/− and −/− animals. d–g) Sections from the spinal cord of GPR17+/− and −/− embryos at E17.5 were immunostained for MBP (d, e) and PDGFRα (f, g). Arrows indicate MBP+ and PDGFRα+ cells, respectively. h–i) Electron micrographs of spinal cross-sections of WT and GPR17−/− mice at P3. Arrows indicate multilamellar myelin sheaths around axons in the lateral white matter. j) Quantitative analysis of myelinated axon fibers in GPR17−/− and WT mice at P3 in the corresponding region of lateral white matter of spinal cord (**P<0.001, Student t-test). k–m) Cortical progenitor cells from WT, GPR17+/− and −/− embryos at E15.5 were cultured to promote oligodendrocyte differentiation. Cells were then immunostained at defined days as indicated for MBP (arrows) and GFP (l–m) or Olig2 (k). n) Quantification of cells expressing MBP from above cultures. All data shown are derived from three experiments in parallel cultures of at least three age-matching littermates (> 1500 cell counts at each stage). Error bars represent SDs. **p<0.001, One-way ANOVA with Newman-Keuls Multiple comparison test. Scale bars: d–g, 100 µm; h–i, 1 µm and k–m, 50 µm.