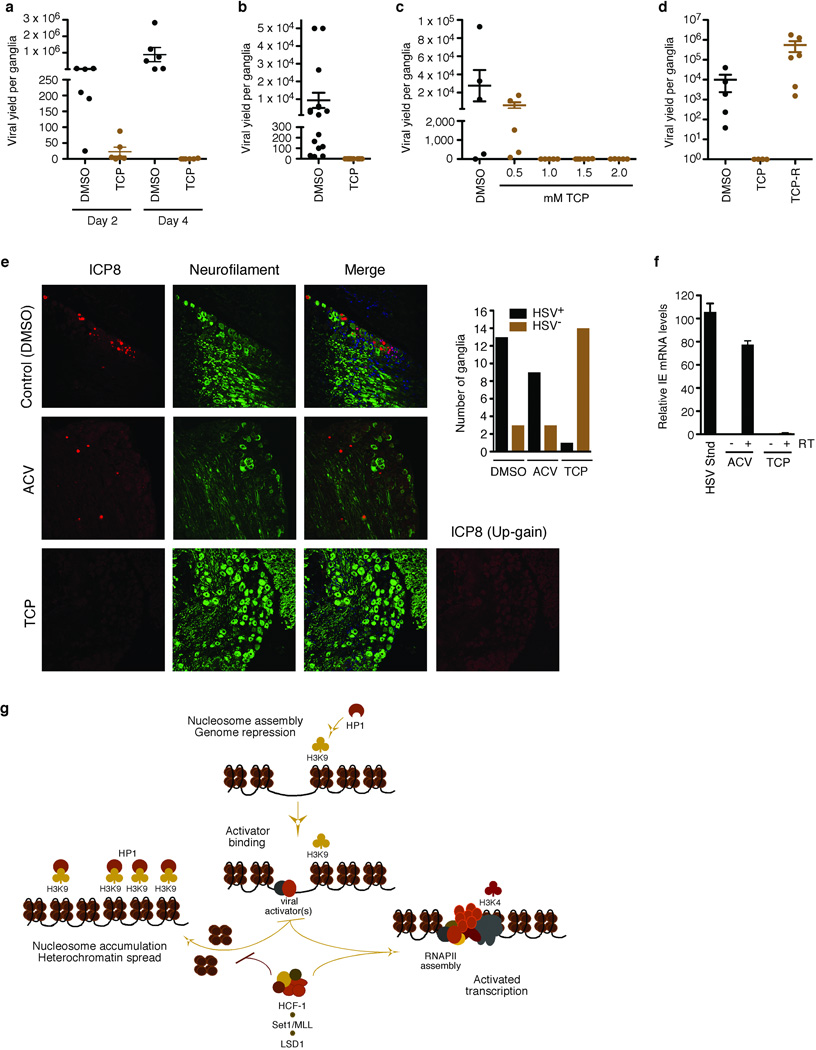
Figure 4. Inhibition of LSD1 with MAOIs blocks HSV-1 reactivation from latency.
(a) Viral yield from ganglia explanted in the absence (DMSO) or presence of 2 mM TCP for 2 days or 4 days. Day 2 P = 0.0043; day 4 P = 0.0011; n=6 for each sample set. (b) Viral yield from paired explanted ganglia in the absence (DMSO) or presence of 2 mM TCP for 2 days. P = 0.0002; n=16 for each sample set. (c) Viral yield from explanted ganglia in the presence or absence (DMSO) of various concentrations of TCP. P < 0.05 for 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 mM TCP while P > 0.05 for 0.5 mM TCP; n=5 for control, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 mM; n=6 for 1.0 mM. (d) Viral yield from explanted ganglia in the absence (DMSO) or presence (TCP) of 2 mM TCP for 2 days followed by incubation in the absence for 3 days (TCP-R). P < 0.025 for TCP vs TCP-R; n=4 for TCP; n=6 for TCP-R. Details of all statistical analyses are in Supplementary Methods. (e) Immunofluorescent staining of HSV-1 latently infected ganglia explanted for 48 hrs in the presence of control (DMSO), 100 uM ACV, or 2 mM TCP. ICP8, HSV single stranded DNA binding protein. For each condition, the number of HSV-1+ and HSV-1− ganglia is shown (P =.00002). (f) Nested RT-PCR analyses of HSV ICP27 IE mRNA from ganglia explanted in the presence of 2 mM TCP or control ACV for 12 hrs. cDNA samples were normalized to the levels of the cellular Sp1 mRNA as determined by qPCR. HSV Stnd represents is the signal from an equivalent amount of control cDNA produced from HSV infected 3T3 cells at 6.4×10−5 pfu/cell. Quantitation was as described in Supplementary Methods. −RT, +RT denote the absence or presence of the reverse transcriptase in the cDNA synthesis reaction. (g) An HCF-1 complex couples LSD1 with Set1/MLL1 to promote α-herpesvirus IE gene transcription. Upon infection, the genomes of infecting α-herpesviruses are subject to the accumulation of repressive chromatin (H3K9 methylation and HP1 occupancy). For productive infection, α-herpesviruses recruit an HCF-1-dependent modification complex containing LSD1 and the H3K4 HMTs Set1/MLL1 to promote the installation of positive transcriptional marks. Failure to recruit this complex results in continued accumulation of nucleosomes bearing repressive H3K9 methylation that silences the viral genome. RNAPII, RNA polymerase II; HP1, heterochromatin protein 1.