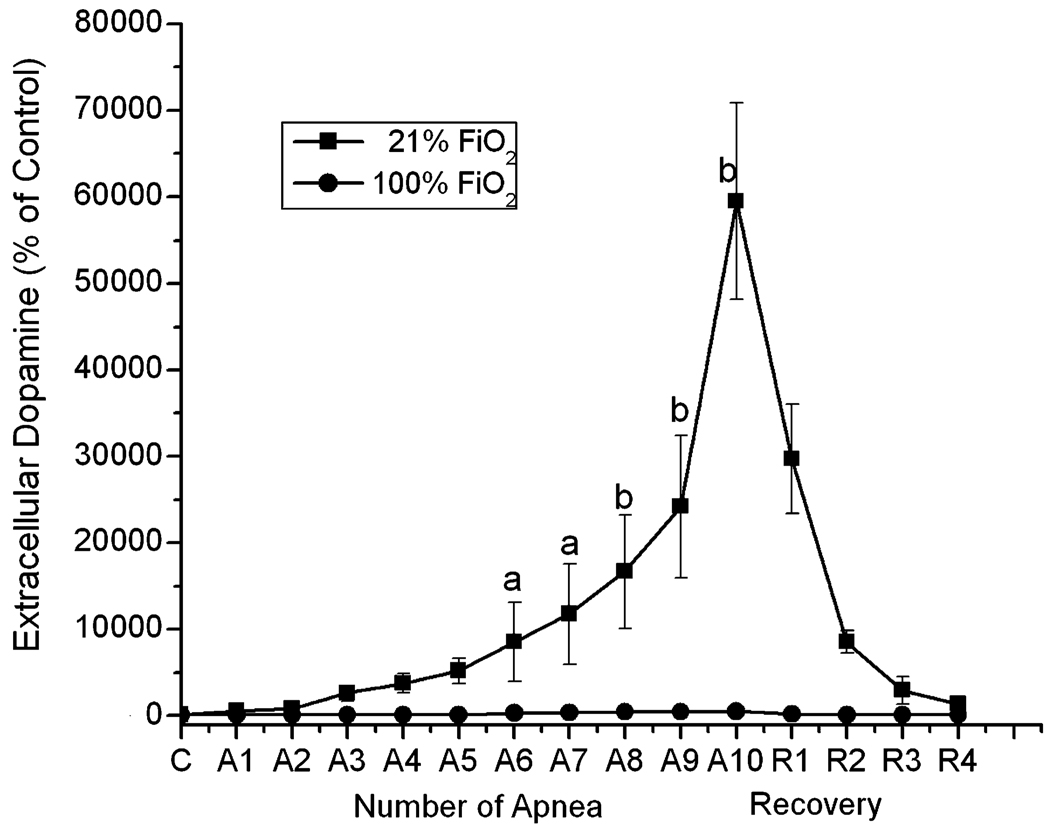
Fig. 4.
The effect of repetitive apnea and resuscitation with 21% oxygen and 100% oxygen on the extracellular concentrations of dopamine in striatum of newborn piglets. The microdialysis probe was implanted in the striatum of newborn piglet and perfused with Ringer solution at 1 µl/min. Collection of the microdialysis samples was initiated 2 h after the probe was inserted and the samples start to be collected from beginning of apnea and ended 1 min after each apneic episodes. R1 and R2 represented 1 h and 2 h of recovery following last apnea. The level of dopamine was analyzed by HPLC with electrochemical detection. The 3 measurements of the dopamine during the pre-apnea period were averaged and the value considered as the baseline (100%). The results are means for 7 experiments in each group ± SD. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.005 for significant difference from control values as determined by one-way analysis of variance, followed by the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.