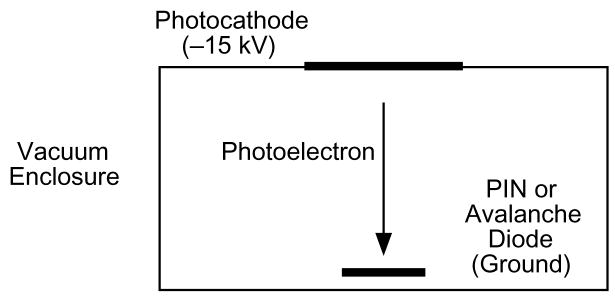
Figure 2.
Diagram of a hybird photodetector. A photon incident on the photocathode liberates a photoelectron. The photocathode is biased 10–15 kV negative with respect to a solid state detector (either a PIN diode or an avalanche diode), which accelerates the electron and causes it to collide with the solid state detector. The electron kinetic energy creates gain, and additional gain can be created in the solid state detector (in the case of the avalanche detector).