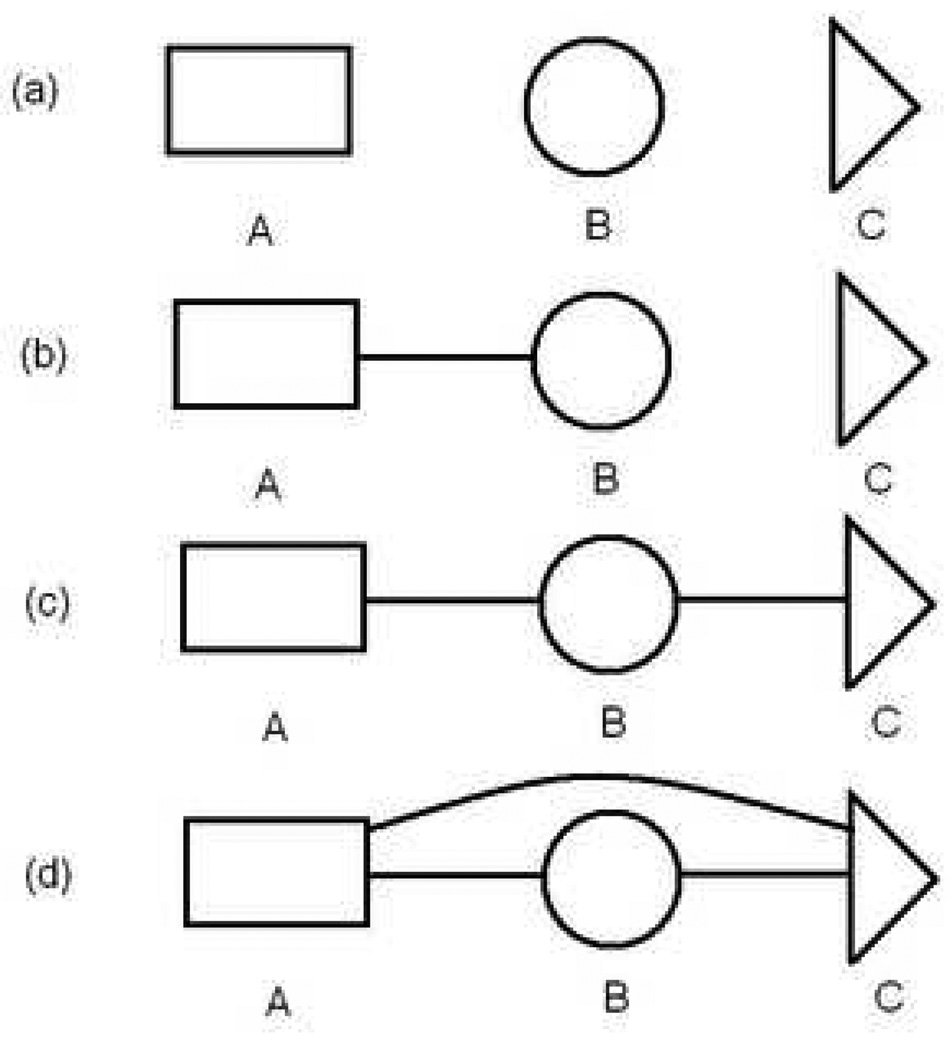
Figure 1.
Stages for calculating the absolute free energy of a molecule by combining three fragments, based on Eq. (9). Connecting lines schematize full interactions between fragments, including both bonded and non-bonded atomistic terms, (a) The first intermediate stage comprises non-interacting fragments, but include all interactions internal to each fragment, (b) The second stage adds interactions among the atoms of fragments A and B, while (c) the third stage does the same for fragments B and C. (d) In the final stage, representing the desired free energy Fphys, all interactions are added, including among non-sequential fragments and possibly including an implicit solvent model.