Fig. 2.
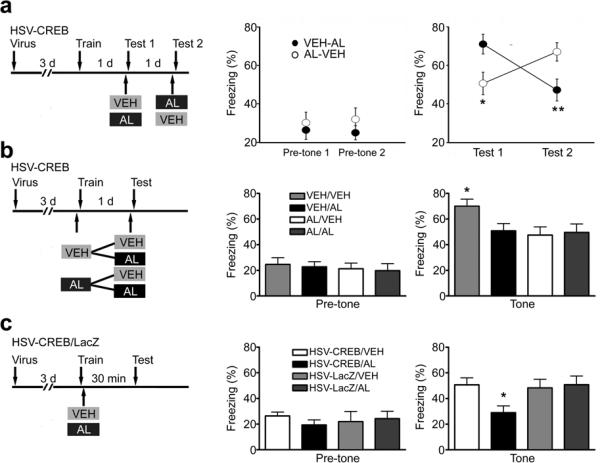
Local infusion of AL selectively impairs auditory fear memory in HSV-CREB mice. (a–c) Left: schematic of the experimental design. Middle: measurements of freezing before tone presentation (pre-tone); Right: measurements of freezing during tone presentation (tone). (a) Histogram showing that the effect of AL is reversible. Mice were tested twice (test 1 and test 2), 1 day apart. The VEH-AL group (n = 17) represents mice that received VEH during test 1 and AL during test 2. The AL-VEH group (n = 15) had the opposite treatment. ** P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05 as indicated. (b) Summary graph shows that although AL during testing impairs freezing in mice free of AL during training (VEH/AL versus VEH/VEH), it has no effect in mice that received AL during training (AL/AL versus AL/VEH). VEH/VEH or AL/AL represents mice that received VEH or AL both during training and testing. VEH (AL)/AL (VEH) represent VEH (AL) during training and AL (VEH) during testing. n = 12 mice for each experimental group. One way ANOVA, F3,44 = 2.96, Fisher's PLSD, *P < 0.05 as indicated. (c) Histogram showing that AL selectively blocks short-term fear memory in HSV-CREB mice. Fisher's PLSD, *P < 0.05, n = 12 mice for each group.
