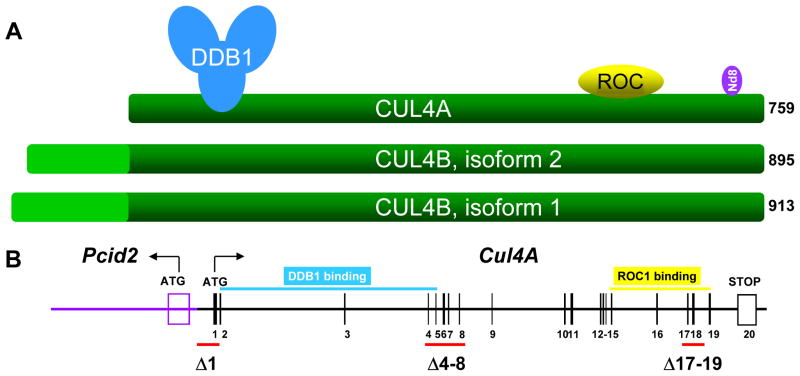
Figure 2. Schematic comparison of CUL4 proteins and mouse Cul4A mutants.
A. Human cells contain two CUL4 genes encoding CUL4A (NP_001008895) and two isoforms of CUL4B (NP_001073341 and NP_003579.3) proteins which differ by only 22 amino acids at the N-terminus.
B. Wild type mouse Cul4A gene and comparison of three targeted Cul4A mutants. Filled and open boxes denote coding and non-coding exons, respectively. Exons encoding the DDB1 and ROC 1 binding regions in CUL4A have been noted. Three mouse models targeting Cul4A have been generated to date, deleting exon 1, exons 4-8, and exons 17-19, respectively. Discrepancies in reported phenotypes might be due to unintentional disruption of a nearby neighboring gene, Pcid2.