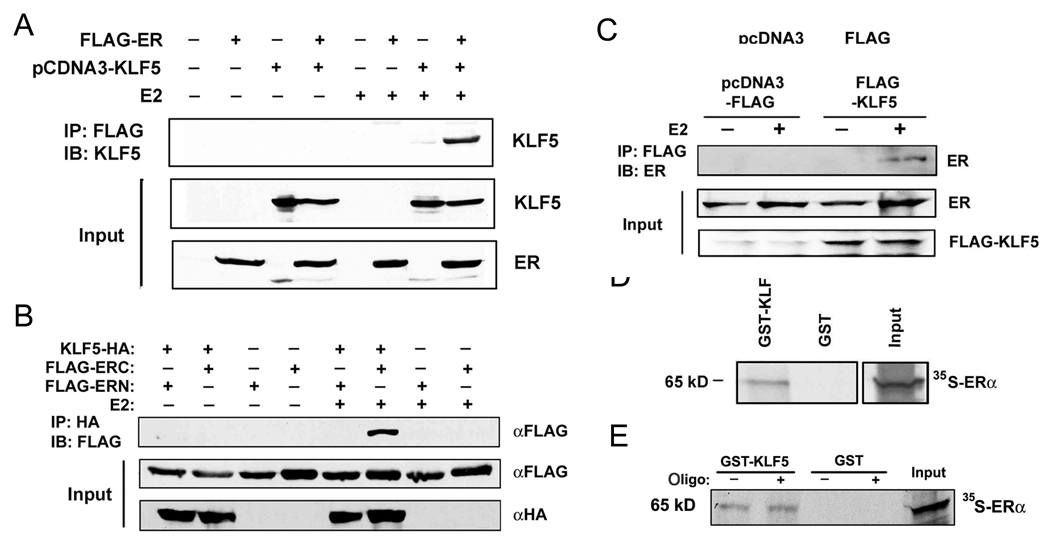
Figure 4. Detection of protein interaction between KLF5 and ERα.
(A) E2 induces protein interaction between KLF5 and ERα in HEK-293 cells transfected with FLAG-tagged ERα and pcDNA3-KLF5 and treated with E2 (1 nM for 20 hour), as detected by immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-FLAG antibody followed by immunoblotting (IB) with antibody against KLF5. (B) E2-induced interaction between KLF5 and ERα involves the C-terminal part of ERα. HEK-293 cells transfected with HA-tagged KLF5 and FLAG-tagged ER fragments (ERN or ERC) were treated with E2 (1 nM for 20 hour), and cell lysates were subjected to IP with anti-HA antibody and IB with anti-FLAG antibody. (C) Interaction between KLF5 and ERα also occurs with endogenous ERα. MCF-7 cells transfected with pcDNA3 empty vector or FLAG-tagged KLF5 and treated with E2 (5 nM for 1 hour) and 10 µM MG132 were subjected to IP with anti-FLAG antibody and IB with antibody against ERα. (D, E) Pull-down of in vitro translated ERα (35S-ERα) by GST-fused KLF5. GST alone serves as a negative control. Annealed double strand oligonucleotides (oligo) containing an ERE were added to the mixture of GST-KLF5 and 35S- ERα (E).