Figure 1. Recruitment of the 43S pre-initiation complex in the cap-dependent and cap-independent mechanisms of translation initiation.
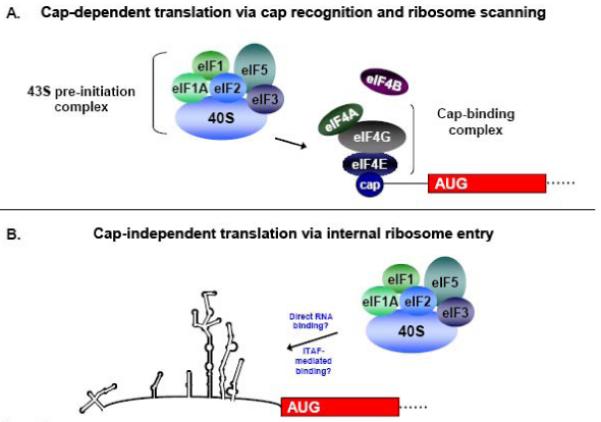
(A) In cap-dependent translation, the eIF4F cap-binding complex recognizes and binds to the 5′ cap structure of the mRNA. Following cap binding, the 43S complex scans the mRNA until an AUG is encountered in a favorable context. After GTP hydrolysis and 60S subunit joining the ribosome is now elongation-competent, and protein synthesis begins. (B) In the cap-independent mechanism of initiation, the 43S pre-initiation complex associates with RNA sequences in the IRES either directly or in conjunction with canonical or non-canonical initiation factors to facilitate initiation at the appropriate AUG start codon. Non-canonical factors are indicated as IRES trans-acting factors, or ITAFs. (Figure adapted from Semler and Waterman, 2008 [100]).
