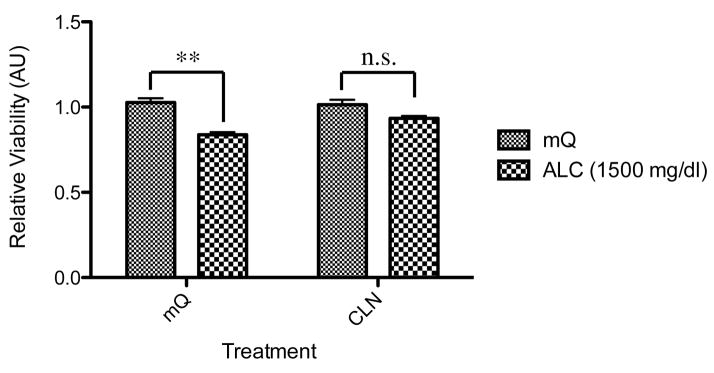
Figure 1.
Effect of colivelin (CLN) against the effects of alcohol exposure in primary cortical neurons (PCNs). PCNs were treated with or without CLN together with or without alcohol. Relative viability measured with WST-8 is shown as means ± SEM (n=3). The two-way ANOVA (p<0.05) demonstrated a significant difference between groups (for alcohol exposure, ALC, F(1,16)=37.26 [p<0.0001]; for CLN treatment, F(1,16)=3.626 [p=0.0750]; for interaction, F(1,16)=6.060 [p=0.256]). Values are shown as mean ± SEM. * p<0.05, n.s. means no significant difference (Newman-Keul’s post hoc test). mQ: autoclaved milli-Q grade water.