Figure 10.
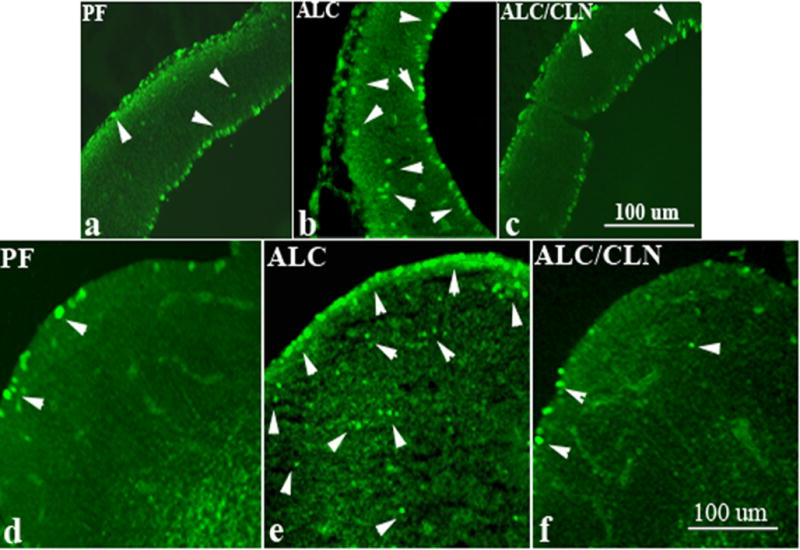
Prenatal alcohol exposure increases the number of p-JNK-positive cells in primordium frontal cortex (b) and basal ganglia eminence (e) of E13 fetal brains in the ALC group as compared to the control group (a, d). Administration of colivelin (CLN) alongside alcohol exposure prevented alcohol-induced increases in TUNEL-positive cells in both regions (c, f). Arrowheads indicate cells expressing p-JNK positive staining. Scale bars: 100 μm.
