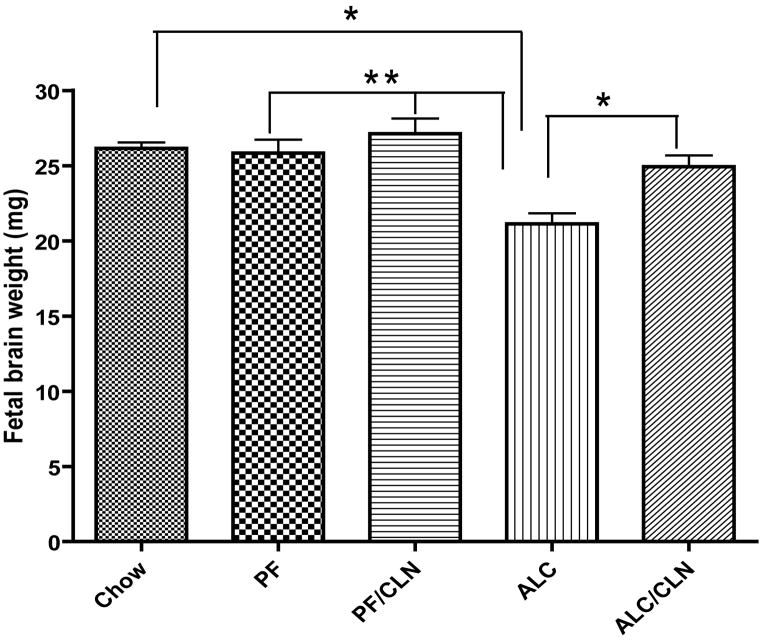
Figure 5.
Protective effect of colivelin (CLN) on fetal brain weight in mice exposed prenatally to alcohol. The one-way ANOVA demonstrated a significant difference between groups (p=0.0001). Prenatal alcohol exposure induced significant fetal brain reduction as compared to the Chow, PF, and PF/CLN control groups (p<0.01, p<0.001, and p<0.001 respectively). CLN treatment prevented the reduction in fetal brain weight found in the ALC group (p<0.05). No significant differences were found between the Chow, PF, PF/CLN, and ALC/CLN groups. Values are shown as mean ± SEM. (Chow, n=5; PF, n=9; PF/CLN, n=5; ALC, n=8; ALC/CLN, n=6). * p<0.01, ** p<0.001 (Newman-Keul’s post hoc test).